


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
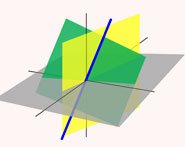
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 2-11-2016
Date: 5-11-2016
Date: 23-10-2016
|
Died: 22 June 1892 in Paris, France

Pierre Bonnet attended the Collège in Montpellier, then in 1838 he entered the École Polytechnique in Paris. He also studied at the École des Ponts et des Chaussées and on graduating he was offered a post as an engineer. After some thought Bonnet decided on a career in teaching and research in mathematics instead.
Turning down the engineering post had not been an easy decision since Bonnet was not well off financially. He had to do private tutoring so that he could afford to accept a position at the École Polytechnique in 1844.
One year before this, in 1843, Bonnet had written a paper on the convergence of series with positive terms. Another paper on series in 1849 was to earn him an award from the Brussels Academy. However between these two papers on series, Bonnet had begun his work on differential geometry in 1844.
Bonnet was elected to the Academy of Sciences in 1862 to replace Biot. He defeated Bour for this position. From 1868 Bonnet assisted Chasles at the École Polytechnique, and three years later he became a director of studies there. In addition to this post he also taught at the École Normale Supérieure.
In 1878 Bonnet succeeded Le Verrier to the chair at the Sorbonne, then in 1883 he succeeded Liouville as a member of the Bureau des Longitudes.
Bonnet did important work on differential geometry. In addition Serret, Frenet, Bertrand and Puiseux worked in France on this topic. Bonnet made major contributions introducing the notion of geodesic curvature. A formula for the line integral of the geodesic curvature along a closed curve is known as the Gauss-Bonnet theorem. Gauss published a special case.
Independently of Minding, Bonnet showed the invariance of the geodesic curvature under bending. Between 1844 and 1867 he published a series of papers on the differential geometry of surfaces. In 1859 he submitted an important memoir for the Grand Prize of the Paris Academy. The prize was
to find all surfaces of a given linear element
and Bour and Codazzi were also entrants. Bonnet's work used a special coordinate system an a surface such as isothermic and tangential coordinates.
Bonnet also published on cartography, algebra, rational mechanics and mathematical physics.
Articles:

|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|