
Isotopes: Varying neutrons
 المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
 المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 31
الجزء والصفحة:
p 31
 28-12-2016
28-12-2016
 1697
1697
Isotopes: Varying neutrons
The atoms of a particular element can have an identical number of protons and electrons but varying numbers of neutrons. If they have different numbers of neutrons, then the atoms are called isotopes.
Hydrogen is a common element here on Earth. Hydrogen’s atomic number is 1 — its nucleus contains 1 proton. The hydrogen atom also has 1 electron. Because it has the same number of protons as electrons, the hydrogen atom is neutral (the positive and negative charges have canceled each other out).
However, approximately one hydrogen atom out of 6,000 contains a neutron in its nucleus. These atoms are still hydrogen, because they each have one proton; they simply have a neutron as well, which most hydrogen atoms lack. So these atoms are called isotopes. Figure 1.1b shows an isotope of hydrogen, commonly called deuterium. It’s still hydrogen, because it contains only one proton, but it’s different from the hydrogen in Figure 1.1a, because it also has one neutron. Because it contains one proton and one neutron, its mass number is 2 amu.
There’s even an isotope of hydrogen containing two neutrons. This one’s called tritium, and it’s represented in Figure 1.1c. Tritium is extremely rare, but it can easily be created. Figure 1.1 also shows an alternative way of representing isotopes: Write the element symbol, a dash, and then the mass number.
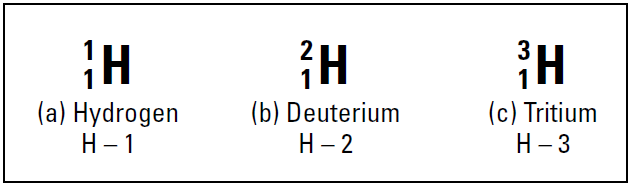
Figure 1.1: The isotopes of hydrogen.
Now you may be wondering, “If I’m doing a calculation involving atomic mass, which isotope do I use?” Well, you use an average of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element but not a simple average. Instead, you use a weighted average, which takes into consideration the abundances of the naturally occurring isotopes. You find this number on the periodic table.
For hydrogen, you have to take into consideration that there’s a lot more H-1 than H-2 and only a very tiny amount of H-3. That’s why the atomic mass of hydrogen on the periodic table isn’t a whole number: It’s 1.0079 amu. The number shows that there’s a lot more H-1 than H-2 and H-3.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


