
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The Biot-Savart law
المؤلف:
Richard Fitzpatrick
المصدر:
Classical Electromagnetism
الجزء والصفحة:
p 92
3-1-2017
2307
The Biot-Savart law
According to above as

we can obtain an expression for the electric field generated by stationary charges by taking minus the gradient of
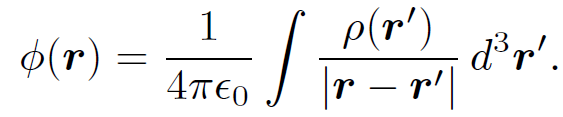
This yields
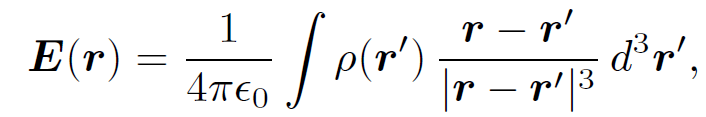 (1.1)
(1.1)
which we recognize as Coulomb's law written for a continuous charge distribution. According to above as
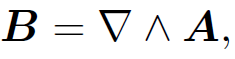
we can obtain an equivalent expression for the magnetic field generated by steady currents by taking the curl of
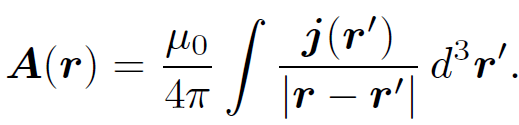
This gives
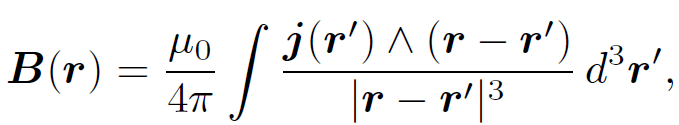 (1.2)
(1.2)
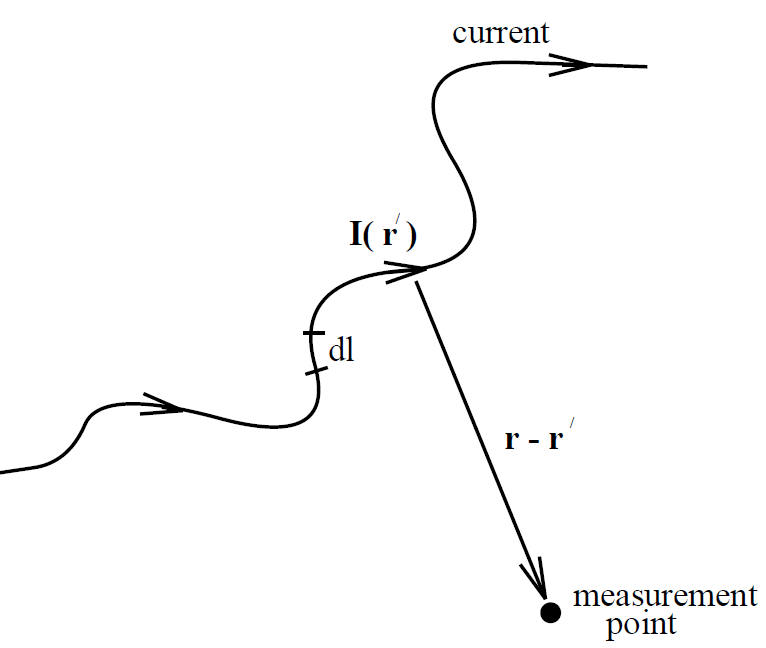
where use has been made of the vector identity ∇ ˄ (ϕA) = ϕ∇ ˄ A + ∇ϕ ˄ A. Equation (1.2) is known as the ''Biot-Savart law" after the French physicists Jean Baptiste Biot and Felix Savart; it completely specifies the magnetic field generated by a steady (but otherwise quite general) distributed current. Let us reduce our distributed current to an idealized zero thickness wire. We can do this by writing
 (1.3)
(1.3)
where I is the vector current (i.e., its direction and magnitude specify the direction and magnitude of the current) and dl is an element of length along the wire. Equations (1.2) and (1.3) can be combined to give
 (1.4)
(1.4)
which is the form in which the Biot-Savart law is most usually written. This
law is to magnetostatics (i.e., the study of magnetic fields generated by steady currents) what Coulomb's law is to electrostatics (i.e., the study of electric fields generated by stationary charges). Furthermore, it can be experimentally verified given a set of currents, a compass, a test wire, and a great deal of skill and patience. This justifies our earlier assumption that the field above as
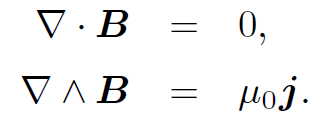
are valid for general current distributions (recall that we derived them by studying the fields generated by infinite, straight wires). Note that both Coulomb's law and the Biot-Savart law are ''gauge independent"; i.e., they do not depend on the particular choice of gauge. Consider (for the last time!) an infinite, straight wire directed along the z-axis and carrying a current I. Let us reconstruct the magnetic field generated by
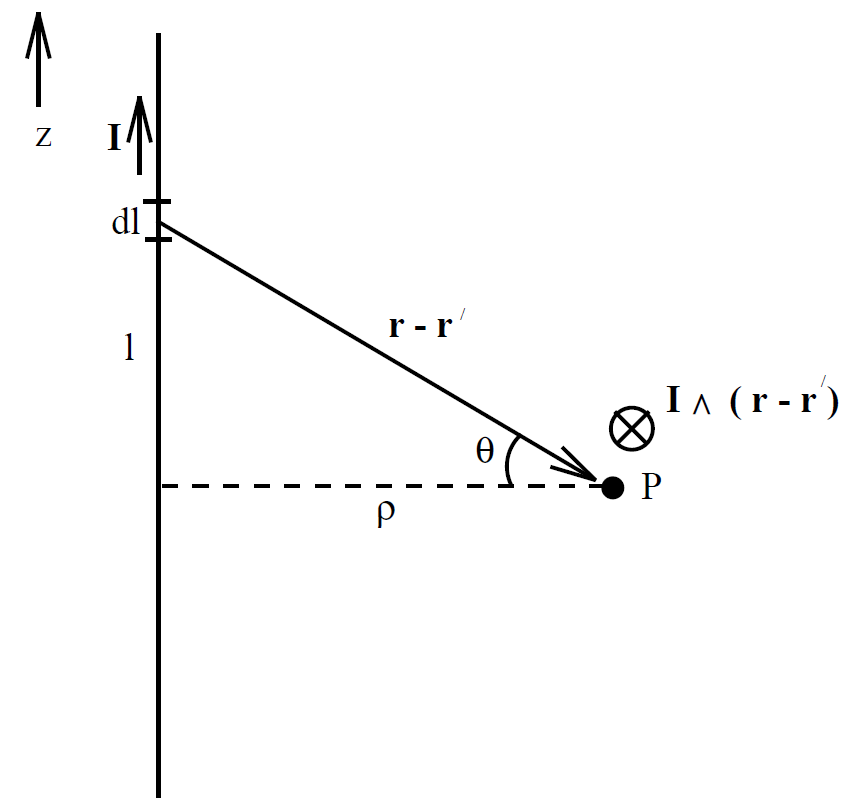
the wire at point P using the Biot-Savart law. Suppose that the perpendicular distance to the wire is ρ. It is easily seen that
 (1.5)
(1.5)
Thus, according to Eq. (1.4) we have
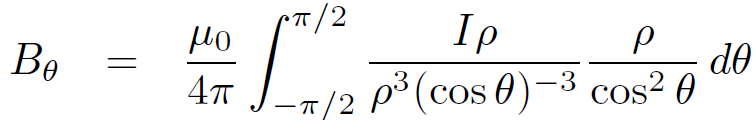
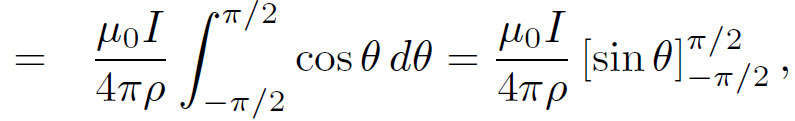 (1.6)
(1.6)
which gives the familiar result
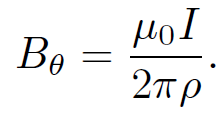 (1.7)
(1.7)
So, we have come full circle in our investigation of magnetic fields. Note that the simple result (1.7) can only be obtained from the Biot-Savart law after some non-trivial algebra. Examination of more complicated current distributions using this law invariably leads to lengthy, involved, and extremely unpleasant calculations.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهرومغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهرومغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















