
Sulfur: reactivity
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 440
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 440
 12-3-2017
12-3-2017
 1575
1575
Sulfur: reactivity
Sulfur is a reactive element. It burns in air with a blue flame to give SO2, and reacts with F2, Cl2 and Br2 (equation 1.1).F or the syntheses of other halides and oxides.
 (1.1)
(1.1)
Sulfur does not react directly with I2, but in the presence of SbF5, the salt [S7I][SbF6] is produced; the cation [S7I]+ possesses structure 1.1. When treated with hot aqueous alkali, sulfur forms a mixture of polysulfides, [Sx]2- , and polythionates( 1.2), while oxidizing agents convert it to H2SO4.
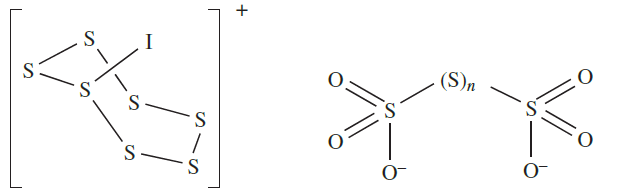
(1.1) (1.2)
Saturated hydrocarbons are dehydrogenated when heated with sulfur, and further reaction with alkenes occurs. An application of this reaction is in the vulcanization of rubber, in which soft rubber is toughened by cross-linking of the polyisoprene chains, making it suitable for use in, for example, tyres. The reactions of sulfur with CO or [CN]- yield OCS (1.3) or the thiocyanate ion (1.4), while treatment with sulfites gives thiosulfates (equation 1.2).
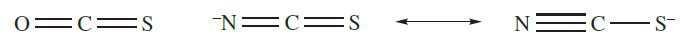
(1.3) (1.4)
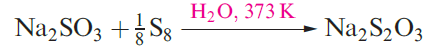 (1.2)
(1.2)
The oxidation of S8 by AsF5 or SbF5 in liquid SO2 yields salts containing the cations [S4]2+, [S8]2+ (Figure 1.1a) and [S19]2+. In reaction 1.3, AsF5 acts as an oxidizing agent and a fluoride acceptor (equation 1.4).

Fig. 1.1 (a) Schematic representation of the structure of [S8]2+. (b) The change in conformation of the ring during oxidation of S8 to [S8]2+. (c) Structural parameters for [S8]2+ from the [AsF6]- salt. (d) One resonance structure that accounts for the transannular interaction in [S8]2+. (e) Schematic representation of the structure of [S19]2+; the rings are puckered.
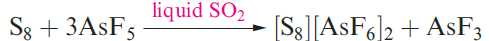 (1.3)
(1.3)
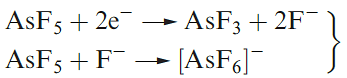 (1.4)
(1.4)
Two-electron oxidation of S8 results in a change in ring conformation (Figure 1.1a). The red [S8]2+ cation was originally reported as being blue, but the blue colour is now known to arise from the presence of radical impurities such as [S5]. In S8, all the S_S bond lengths are equal (206 pm) and the distance between two S atoms across the ring from one another is greater than the sum of the van der Waals radii (rv = 185 pm). The structure of the [AsF6]- salt of [S8]2+ has been determined and Figure 1.1c illustrates (i) a variation in S_S bond distances around the ring and (ii) cross-ring S_S separations that are smaller than the sum of the van der Waals radii, i.e. [S8]2+ exhibits transannular interactions. The most important transannular interaction corresponds to the shortest S…..S contact and Figure 1.1d shows a resonance structure that describes an appropriate bonding contribution. The [S4]2+ cation is square (S_S = 198pm) with delocalized bonding. In [S19]2+ (Figure 1.1e), two 7-membered, puckered rings are connected by a five-atom chain. The positive charge can be considered to be localized on the two 3-coordinate S centres.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


