


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 16-12-2020
Date: 16-12-2020
Date: 3-4-2017
|
Binding Energy Per Nucleon (BE/A)
As the number of particles in a nucleus increases, the total binding energy also increases. The rate of increase, however, is not uniform. This lack of uniformity results in a variation in the amount of binding energy associated with each nucleon within the nucleus. This variation in the binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) is easily seen when the average BE/A is plotted versus atomic mass number (A), as shown in Figure 1.
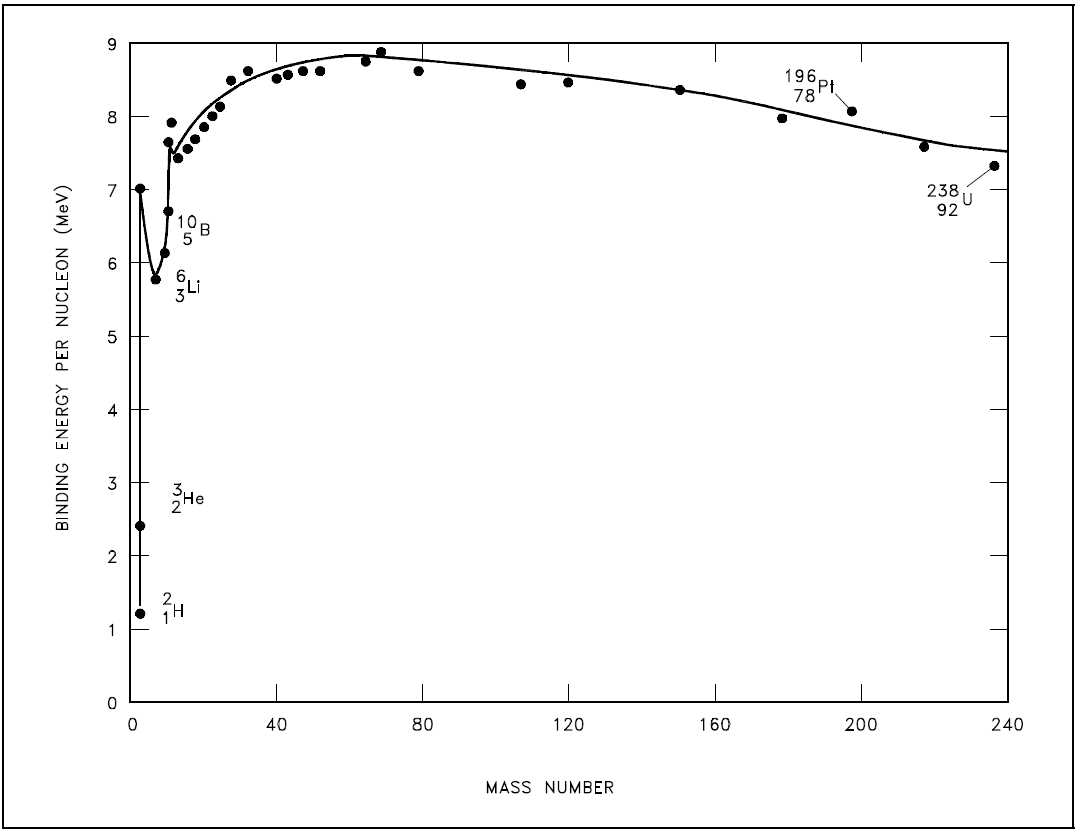
Figure 1: Binding Energy per Nucleon vs. Mass Number
Figure 1 illustrates that as the atomic mass number increases, the binding energy per nucleon decreases for A > 60. The BE/A curve reaches a maximum value of 8.79 MeV at A = 56 and decreases to about 7.6 MeV for A = 238. The general shape of the BE/A curve can be explained using the general properties of nuclear forces. The nucleus is held together by very short-range attractive forces that exist between nucleons. On the other hand, the nucleus is being forced apart by long range repulsive electrostatic (coulomb) forces that exist between all the protons in the nucleus.
As the atomic number and the atomic mass number increase, the repulsive electrostatic forces within the nucleus increase due to the greater number of protons in the heavy elements. To overcome this increased repulsion, the proportion of neutrons in the nucleus must increase to maintain stability. This increase in the neutron-to-proton ratio only partially compensates for the growing proton-proton repulsive force in the heavier, naturally occurring elements. Because the repulsive forces are increasing, less energy must be supplied, on the average, to remove a nucleon from the nucleus. The BE/A has decreased. The BE/A of a nucleus is an indication of its degree of stability. Generally, the more stable nuclides have higher BE/A than the less stable ones. The increase in the BE/A as the atomic mass number decreases from 260 to 60 is the primary reason for the energy liberation in the fission process. In addition, the increase in the BE/A as the atomic mass number increases from 1 to 60 is the reason for the energy liberation in the fusion process, which is the opposite reaction of fission.
The heaviest nuclei require only a small distortion from a spherical shape (small energy addition) for the relatively large coulomb forces forcing the two halves of the nucleus apart to overcome the attractive nuclear forces holding the two halves together. Consequently, the heaviest nuclei are easily fissionable compared to lighter nuclei.



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية تستعدّ لتكريم عددٍ من الطالبات المرتديات للعباءة الزينبية في جامعات كركوك
|
|
|