
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Effective Multiplication Factor
المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
الجزء والصفحة:
p 8
17-4-2017
2858
Effective Multiplication Factor
The infinite multiplication factor can fully represent only a reactor that is infinitely large, because it assumes that no neutrons leak out of the reactor. To completely describe the neutron life cycle in a real, finite reactor, it is necessary to account for neutrons that leak out. The multiplication factor that takes leakage into account is the effective multiplication factor (keff), which is defined as the ratio of the neutrons produced by fission in one generation to the number of neutrons lost through absorption and leakage in the preceding generation.
The effective multiplication factor may be expressed mathematically as shown below.

So, the value of keff for a self-sustaining chain reaction of fissions, where the neutron population is neither increasing nor decreasing, is one. The condition where the neutron chain reaction is self-sustaining and the neutron population is neither increasing nor decreasing is referred to as the critical condition and can be expressed by the simple equation keff = 1 . If the neutron production is greater than the absorption and leakage, the reactor is called supercritical. In a supercritical reactor, keff is greater than one, and the neutron flux increases each generation. If, on the other hand, the neutron production is less than the absorption and leakage, the reactor is called subcritical. In a subcritical reactor, keff is less than one, and the flux decreases each generation.
When the multiplication factor of a reactor is not equal to exactly one, the neutron flux will change and cause a change in the power level. Therefore, it is essential to know more about how this factor depends upon the contents and construction of the reactor. The balance between production of neutrons and their absorption in the core and leakage out of the core determines the value of the multiplication factor. If the leakage is small enough to be neglected, the multiplication factor depends upon only the balance between production and absorption, and is called the infinite multiplication factor (k∞) since an infinitely large core can have no leakage. When the leakage is included, the factor is called the effective multiplication factor (keff).
The effective multiplication factor (keff) for a finite reactor may be expressed mathematically in terms of the infinite multiplication factor and two additional factors which account for neutron leakage as shown below.
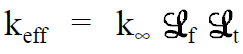
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















