
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Samarium-149 Response to Reactor Shutdown
المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
الجزء والصفحة:
p 45
21-4-2017
2870
Samarium-149 Response to Reactor Shutdown
Since the neutron flux drops to essentially zero after reactor shutdown, the rate of samarium-149 production becomes the following.
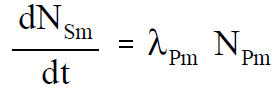
Because samarium-149 is not radioactive and is not removed by decay, it presents problems somewhat different from those encountered with xenon-135, as illustrated in Figure 1. The equilibrium concentration and the poisoning effect build to an equilibrium value during reactor operation. This equilibrium is reached in approximately 20 days (500 hours), and since samarium-149 is stable, the concentration remains essentially constant during reactor operation. When the reactor is shutdown, the samarium-149 concentration builds up as a result of the decay of the accumulated promethium-149. The buildup of samarium-149 after shutdown depends upon the power level before shutdown. Samarium-149 does not peak as xenon-135 does, but increases slowly to a maximum value as shown in Figure 1. After shutdown, if the reactor is then operated at power, samarium-149 is burned up and its concentration returns to the equilibrium value. Samarium poisoning is minor when compared to xenon poisoning. Although samarium-149 has a constant poisoning effect during long-term sustained operation, its behavior during initial startup and during post-shutdown and restart periods requires special considerations in reactor design.
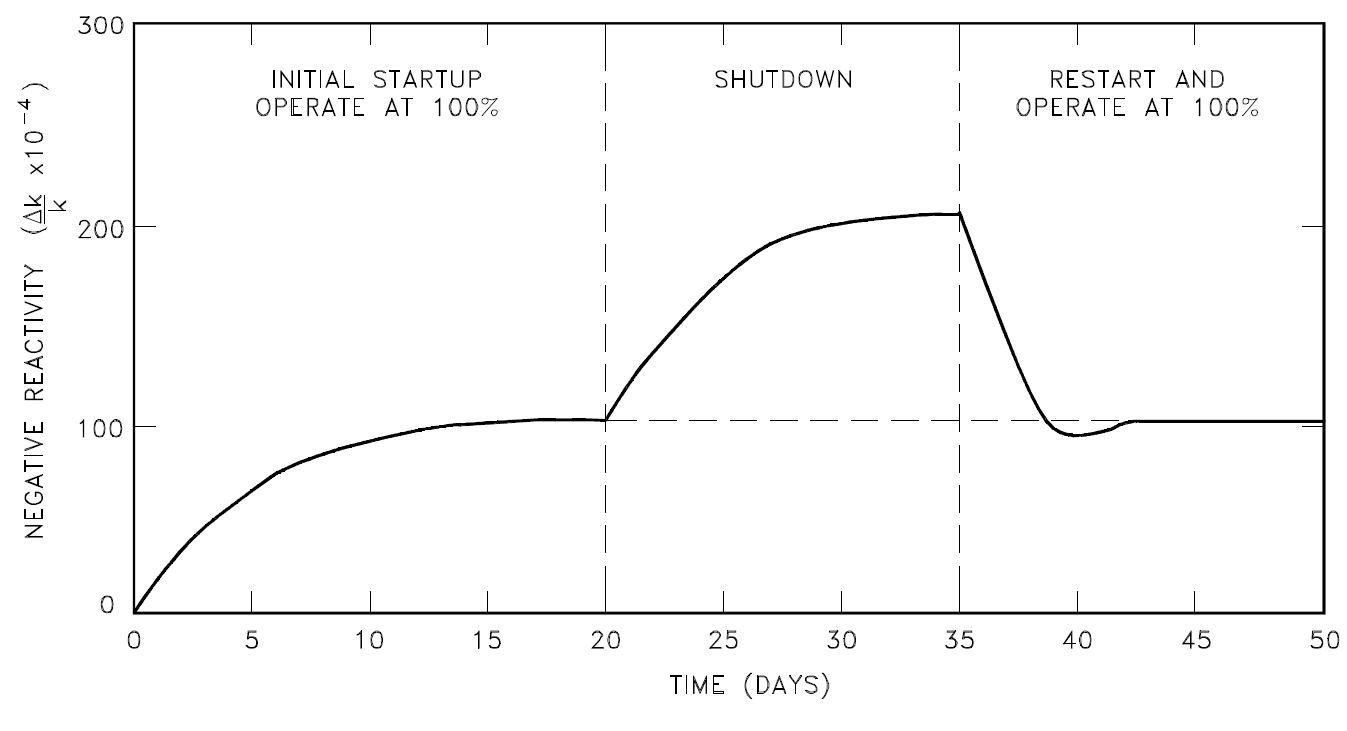
Figure 1: Behavior of Samarium-149 in a Typical Light Water Reactor
The xenon-135 and samarium-149 mechanisms are dependent on their very large thermal neutron cross sections and only affect thermal reactor systems. In fast reactors, neither these nor any other fission products have a major poisoning influence.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















