
The Potential Barrier
 المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
 المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 42
الجزء والصفحة:
p 42
 9-5-2017
9-5-2017
 2796
2796
The Potential Barrier
We now want to consider the potential barrier function, which is shown in Figure 1.1. The more interesting problem, again, is in the case when the total energy of an incident particle is E < V0. Again assume that we have a flux of incident particles originating on the negative x axis traveling in the +x direction. As before, we need to solve Schrodinger's time-independent wave equation in each of the three regions. The
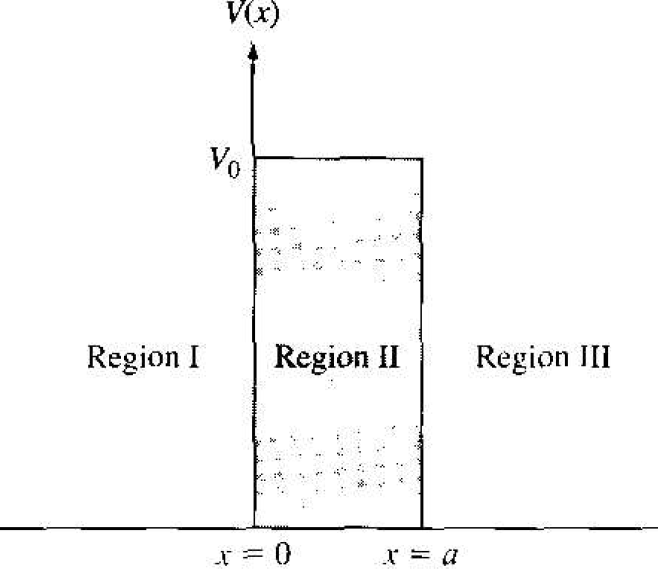
Figure 1.1 The potential barrier function.
solutions of the wave equation in regions I, II, and III are given, respectively, as
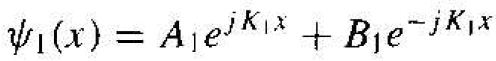 (1a)
(1a)
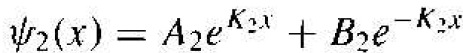 (1b)
(1b)
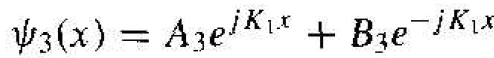 (1c)
(1c)
where
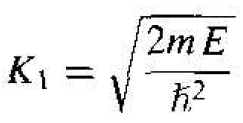 (2a)
(2a)
and
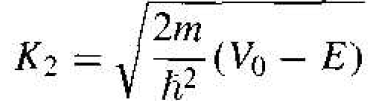 (2b)
(2b)
The coefficient B3 in Equation (1c)e presents a negative traveling wave in region III. However, once a particle gets into region III, there are no potential changes to cause a reflection; therefore, the coefficient B3 must be zero. We must keep both exponential terms in Equation (1b) since the potential barrier width is finite; that is, neither term will become unbounded. We have four boundary relations for the boundaries at x = 0 and x = a corresponding to the wave function and its first derivative being continuous. We can solve for the four coefficients B1, A2, B2. and A2 in terms of A1 . The wave solutions in the three regions are shown in Figure 1.2.
One particular parameter of interest is the transmission coefficient, in this case defined as the ratio of the transmitted flux in region III to the incident flux in region I. Then the transmission coefficient T is
 (3)
(3)
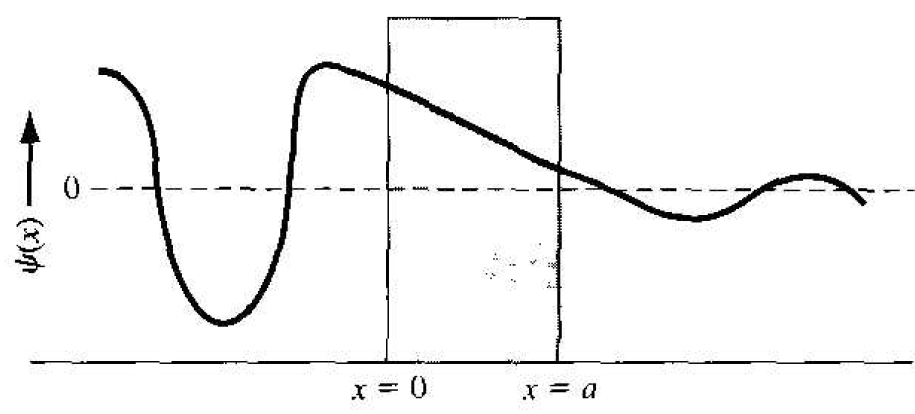
Figure 1.2 The wave functions through the potential barrier.
where vr and vi are the velocities of the transmitted and incident particles, respectively. Since the potential V = 0 in both regions I and III, the incident and transmitted velocities are equal. The transmission coefficient may be determined by solving the boundary condition equations. For the special case when E << V0, we find that
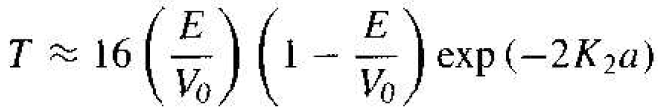 (4)
(4)
Equation (4) implies that there is a finite probability that a particle impinging a potential barrier will penetrate the barrier and will appear in region III. This phenomenon is called tunneling and it, too, contradicts classical mechanics. We will see later how this quantum mechanical tunneling phenomenon can be applied to semiconductor device characteristics, such as in the tunnel diode.
 الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


