
Calculation of pH of a Solution of an Acid or Base
 المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
 المصدر:
College Chemistry
المصدر:
College Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 120
الجزء والصفحة:
p 120
 17-7-2017
17-7-2017
 2154
2154
Calculation of pH of a Solution of an Acid or Base
In performing a calculation based on an acid or base ionization constant expression ,there are often many unknowns. Remember that in an algebraic problem involving multiple unknowns, one needs as many equations as there are unknowns. The equilibrium constant expression itself is one equation, and the Kw expression is always available. Two other types of equation are often useful: equations expressing conservation of atoms or groups of atoms, and an equation expressing the charge neutrality of the solution.
Example 1
Compute the pH and the concentrations of the various species present in a 0.10 M solution of formic acid, HCOOH.
The species present in this solution are HCOOH, HCO2-, H3O+, and OH-. With four unknowns, we need four equations: Equilibrium constant expressions:
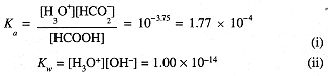

Conservation of charge:
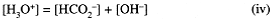
We expect the solution to be at least weakly acidic, which suggests that [OH-] << [H3O+] so that we can ignore [OH-] in Eq. (iv). Equations (iv) and (iii) give [H3O+] = [HCO2-] = x and [HCOOH] = 0.10 - x. We can
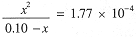
Substituting into the equilibrium constant expression,
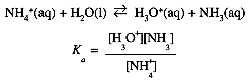
Solving the quadratic equation gives x = 4.12 × 10-3 or -4.30 × 10-3. The negative root makes no sense and we conclude that [H3O+] = [HCO2-] = 4.12 × 10-3 M, [HCOOH] = 0.096 M, pH = 2.38. Equation (ii) then gives [OH-] = 2.43 × 10-12 M. Here x is not quite small enough to ignore compared with 0.10, but in other problems where Ka is smaller, it may be a reasonable approximation.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


