

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Halides of Group 1 elemants
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 263
15-1-2018
1852
Halides of Group 1 elemants
The MX halides are prepared by direct combination of the elements ) and all the halides have large negative ΔfHo values. However, Table 1.1 shows that for X = F, values of ΔfHo (MX) become less negative down the group, while the reverse trend is true for X= Cl, Br and I. For a given metal, ΔfHo(MX) always becomes less negative on going from MF to MI. These generalizations can be explained in terms of a Born–Haber cycle.
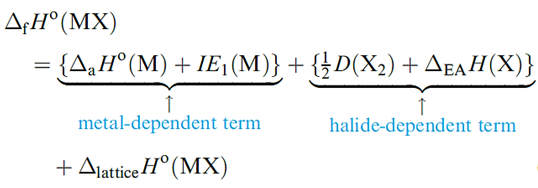
For MF, the variable quantities are ΔaHo(M), IE1(M) and ΔlatticeHo(MF), and similarly for each of MCl, MBr and MI. The sum of ΔaHo(M) and IE1(M) gives for the formation of Li+ 681, of Na+ 604, of K+ 509, of Rb+ 485 and of Cs+ 454 kJ mol_1.
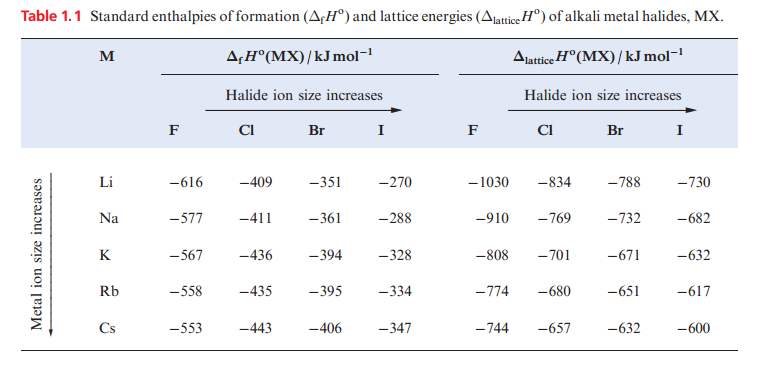
For the fluorides, the trend in the values of ΔfHo(MF) depends on the relative values of {ΔaHo(M) + IE1(M)} and ΔlatticeHo(MF) and similarly for chlorides, bromides and iodides. Inspection of the data shows that the variation in {ΔaHo(M( + IE1)M(} is less than the variation in ΔlatticeHo(MF), but greater than the variation in ΔlatticeHo(MX) for X = Cl, Br and I. This is because lattice energy is proportional to 1 / (r+ + r-) and so variation in ΔlatticeHo(MX) for a given halide is greatest when r_ is smallest (for F-) and least when r_ is largest (for I-). Considering the halides of a given metal the small change in the term {1/2 D(X2) + ΔEAH)X(} (_249, _228, _213, _188 kJ mol_1 for F, Cl, Br, I respectively) is outweighed by the decrease in ΔlatticeHo(MX).
In Table 1.1, note that the difference between the values of ΔfHo(MF) and ΔfHo(MI) decreases significantly as the size of the M ion increases. The solubilities of the alkali metal halides in water are determined by a delicate balance between lattice energies and free energies of hydration. LiF has the highest lattice energy of the group 1 metal halides and is only sparingly soluble, but solubility relationships among the other halides.
The salts LiCl, LiBr, LiI and NaI are soluble in some oxygen-containing organic solvents, e.g. LiCl dissolves in THF and MeOH; complexation of the Li+ or Na+ ion by the O-donor solvents is likely in all cases. Both LiI and NaI are very soluble in liquid NH3, forming complexes; the unstable complex [Na(NH3)4]I has been isolated and contains a tetrahedrally coordinated Na+ ion. In the vapour state, alkali metal halides are present mainly as ion-pairs, but measurements of M_X bond distances and electric dipole moments suggest that covalent contributions to the bonding, particularly in the lithium halides, are important.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















