
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
MICROSCOPE MAGNIFICATION
المؤلف:
S. Gibilisco
المصدر:
Physics Demystified
الجزء والصفحة:
532
11-11-2020
1978
MICROSCOPE MAGNIFICATION
Refer to Fig. 1. Suppose that fo is the focal length (in meters) of the objective lens and fe is the focal length (in meters) of the eyepiece. Assume that the objective and the eyepiece are placed along a common axis and that the distance between their centers is adjusted for proper focus. Let s represent the distance (in meters) from the objective to the real image it forms of the object under examination. The microscopic magnification (a dimensionless quantity denoted m in this context) is given by
m = [(s - fo)/fo)] [(fe + 0.25)/fe]
The quantity 0.25 represents the average near point of the human eye, which is the closest distance over which the eye can focus on an object: approximately 0.25 m.
A less formal method of calculating the magnification of a microscope is to multiply the magnification of the objective by the magnification of the eyepiece. These numbers are provided with objectives and eyepieces and
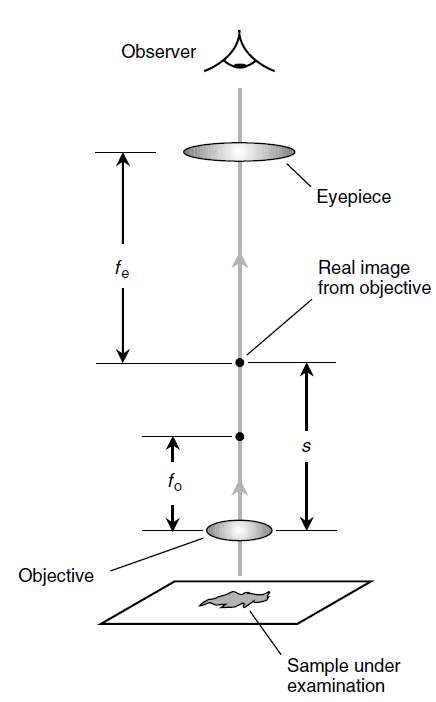
Fig. 1. Calculation of the magnification factor in a compound microscope. See text for details.
are based on the use of an air medium between the objective and the specimen, as well as on the standard distance between the objective and the eyepiece. If me is the power of the eyepiece and mo is the power of the objective, then the power m of the microscope as a whole is
m = memo
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















