
INTRACAVITY SWITCHES
 المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
 المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p195
الجزء والصفحة:
p195
 20-3-2016
20-3-2016
 2826
2826
INTRACAVITY SWITCHES
A Q-switch consists of a mechanism that spoils the resonance of the laser cavity. There are a number of ways to accomplish this, from altering the alignment of a cavity mirror mechanically (e.g., by a rotating mirror), insertion of an optical switch within the cavity of the laser itself (e.g., an EO or AO modulator), or a saturable dye switch within the cavity. These methods are outlined in Figure 1.1, in which each type of Q-switch is shown within in a solid-state laser cavity.
A rotating mirror, the simplest method, is rarely used except in a few older military rangefinders that use ruby rods. A high-speed motor drives the mirror, which, once per revolution, aligns with the other cavity mirror. Just prior to this alignment, the optical pump (usually, a flash lamp) is fired to ensure that a massive population inversion has built up before the cavity is aligned. The shortcoming of this method is that the experiment must be synchronized to the laser, which fires at repeated intervals. Control over when the laser fires is not possible. As well, the pulse is not as formed as other Q-switching methods since the Q of the cavity does not suddenly jump to a maximum value but rather, increases as the mirror rotates and the mirror becomes mechanically close to the optimal alignment position.
Electrooptic and acoustooptic modulators work quite literally as optical switches, allowing intracavity light to pass only when the switch is open. These are controllable and allow the laser to be fired at the operator’s command, as required by many experiments. These modulators, the most popular for Q-switching applications.
Saturable dye switches are simply a cell filled with organic dye (similar to the dye used in a dye laser) placed inside the laser cavity. These work by absorbing intracavity radiation, inducing a large loss in the cavity, until the dye becomes saturated or bleached, at which point it cannot absorb more laser energy and the remaining light passes through the cell to be amplified in the laser (i.e., the laser begins to oscillate). The time it takes to saturate a dye is characteristic of the dye itself and depends on the lifetime of the energy levels in the dye molecule itself.
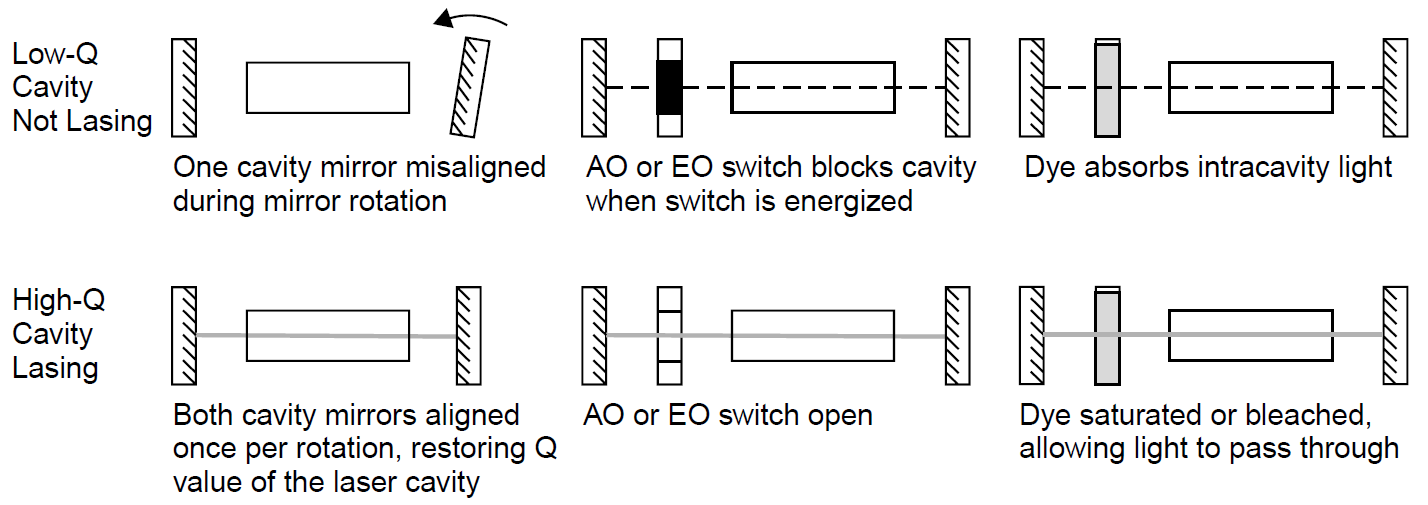
Figure 1.1. Q-switching methods.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


