


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 5-10-2020
Date: 12-10-2020
Date: 31-7-2019
|
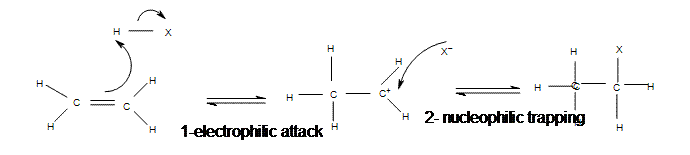
The addition of hydrogen halides is one of the easiest electrophilic addition reactions because it uses the simplest electrophile: the proton. Hydrogen halides provide both a electrophile (proton) and a nucleophile (halide). First, the electrophile will attack the double bond and take up a set of pi electrons, attaching it to the molecule (1). This is basically the reverse of the last step in the E1 reaction (deprotonation step). The resulting molecule will have a single carbon-carbon bond with a positive charge on one of them (carbocation). The next step is when the nucleophile (halide) bonds to the carbocation, producing a new molecule with both the original hydrogen and halide attached to the organic reactant (2). The second step will only occur if a good nucleophile is used.
Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halide to Ethene
Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halide to Propene
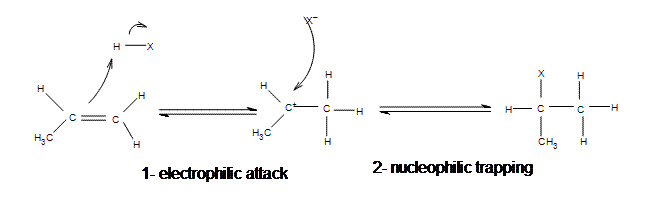
All of the halides (HBr, HCl, HI, HF) can participate in this reaction and add on in the same manner. Although different halides do have different rates of reaction, due to the H-X bond getting weaker as X gets larger (poor overlap of orbitals)s.



|
|
|
|
بـ3 خطوات بسيطة.. كيف تحقق الجسم المثالي؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دماغك يكشف أسرارك..علماء يتنبأون بمفاجآتك قبل أن تشعر بها!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تواصل إقامة مجالس العزاء بذكرى شهادة الإمام الكاظم (عليه السلام)
|
|
|