
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Blackbody Radiation
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner Michael Bass
المصدر:
Solid-state Lasers
الجزء والصفحة:
15
26-1-2021
2373
Blackbody Radiation
When electromagnetic radiation in an isothermal enclosure, or cavity, is in thermal equilibrium at temperature T , the distribution of radiation density 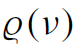 dν, contained in a bandwidth dν, is given by Planck’s law
dν, contained in a bandwidth dν, is given by Planck’s law
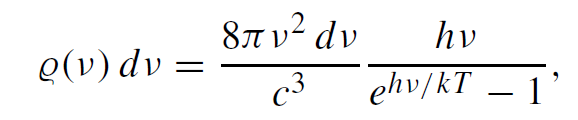 ......(1)
......(1)
where 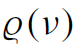 is the radiation density per unit frequency [J s/cm3], k is Boltzmann’s constant, and c is the velocity of light. The spectral distribution of thermal radiation vanishes at ν = 0 and ν → ∞, and has a peak which depends on the temperature.
is the radiation density per unit frequency [J s/cm3], k is Boltzmann’s constant, and c is the velocity of light. The spectral distribution of thermal radiation vanishes at ν = 0 and ν → ∞, and has a peak which depends on the temperature.
The factor
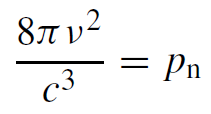 ......(2)
......(2)
in (1) gives the density of radiation modes per unit volume and unit frequency interval. The factor pn can also be interpreted as the number of degrees of freedom associated with a radiation field, per unit volume, per unit frequency interval. The expression for the mode density pn [modes s/cm3] plays an important role in connecting the spontaneous and the induced transition probabilities.
For a uniform, isotropic radiation field, the following relationship is valid
 ..........(3)
..........(3)
where W is the blackbody radiation [W/cm2] which will be emitted from an opening in the cavity of the blackbody. Many solids radiate like a blackbody. Therefore, the radiation emitted from the surface of a solid can be calculated from (3).
According to the Stefan–Boltzmann equation, the total blackbody radiation is
 .......(4)
.......(4)
where σ = 5.68 × 10−12 W/cm2 K4. The emitted radiation W has a maximum which is obtained from Wien’s displacement law
 ........(5)
........(5)
For example, a blackbody at a temperature of 5200 K has its radiation peak at 5564 A° , which is about the center of the visible spectrum.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















