
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Other types of magnetic order
المؤلف:
J. M. D. COEY
المصدر:
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
الجزء والصفحة:
12
10-2-2021
1863
Other types of magnetic order
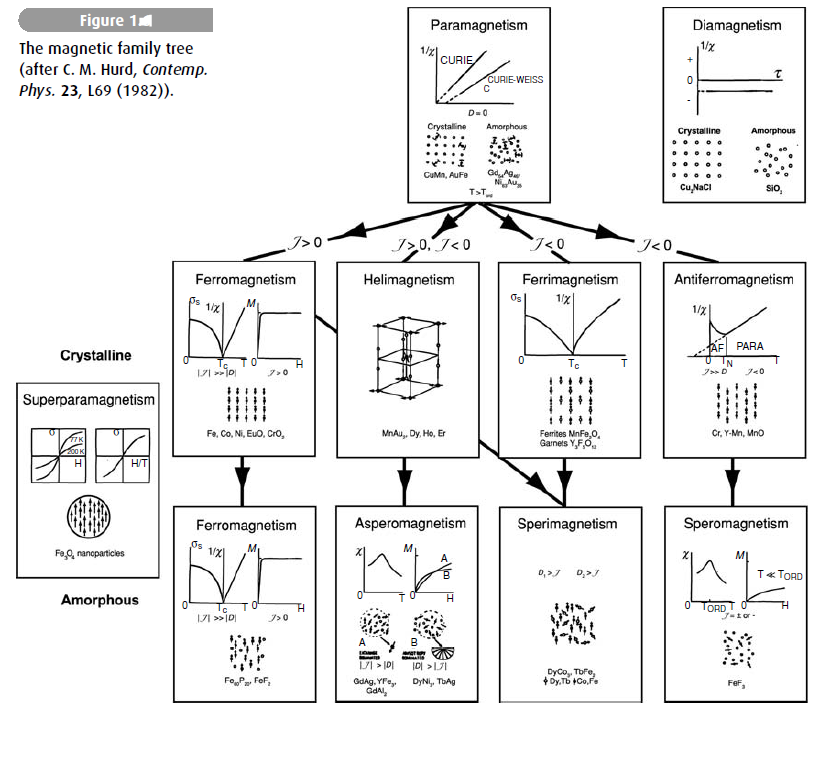
The spontaneous magnetization of a ferromagnet is the result of alignment of the magnetic moments of individual atoms. But parallel alignment is not the only – or even the most common – type of magnetic order. In an antiferromagnet, the atomic moments form two equivalent but oppositely oriented magnetic sublattices. Although Ms = 0, the material nonetheless exhibits a phase transition with a λ-shaped specific heat anomaly where the moments begin to order. The antiferromagnetic transition occurs at the Ne´ el temperature TN. Occasionally it is possible to switch an antiferromagnet into a ferromagnet if a sufficiently large field is applied. This discontinuous change of magnetic order is known as a metamagnetic transition.
If the sublattices are inequivalent, with sublattice magnetizationsMA and MB where MA ≠ −MB, there is a net spontaneous magnetization. The material is a ferrimagnet. Most of the useful magnetic oxides, including magnetite, are ferrimagnetic.
The alignment of the atomic moments in the ordered state need not be collinear. Multiple noncollinear sublattices are found in manganese and some of its alloys. Other materials such as MnSi orMn3Au have helical or spiral magnetic structures that are incommensurate with the underlying crystal lattice. In some disordered and amorphous materials the atomic moments freeze in more or less random directions. Such random, noncollinear magnets are known collectively as spin glasses. The original spin glassses were magnetically dilute crystalline alloys, but several different varieties of random spin freezing are encountered in noncrystalline (amorphous) solids. Finally, we remark on the behaviour of ferromagnetic fine particles whose volume V is so small that the product KuV is less than or comparable to the thermal energy kBT ; in that case the total sum moment, m, of all the coupled atoms fluctuates randomly like that of a large paramagnetic atom or macrospin. The susceptibility follows a Curie law with a huge value of C. The name superparamagnetism was coined by N´eel for this phenomenon, which is important for ferrofluids (magnetic liquids which are really colloidal suspensions of ferrimagnetic fine particles) and in rock magnetism.
Figure 1. portrays the magnetic family tree, summarizing the behaviour of the magnetization or susceptibility for the different types of magnetic order in crystalline and amorphous solids.
 الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
الاكثر قراءة في المغناطيسية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















