


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 29-3-2021
Date: 25-3-2021
Date: 25-3-2021
|
Present Perfect
Definition of the present perfect tense
The present perfect is used to indicate a link between the present and the past. The time of the action is before now but not specified, and we are often more interested in the result than in the action itself.
BE CAREFUL! There may be a verb tense in your language with a similar form, but the meaning is probably NOT the same.
The Present Perfect is used to describe
An action or situation that started in the past and continues in the present. I have lived in Bristol since 1984 (= and I still do.)
An action performed during a period that has not yet finished. She has been to the cinema twice this week (= and the week isn't over yet.)
A repeated action in an unspecified period between the past and now. We have visited Portugal several times.
An action that was completed in the very recent past, expressed by 'just'. I have just finished my work.
An action when the time is not important. He has read 'War and Peace'. (= the result of his reading is important)
Note: When we want to give or ask details about when, where, who, we use the simple past.
Actions started in the past and continuing in the present
They haven't lived here for years.
She has worked in the bank for five years.
We have had the same car for ten years.
Have you played the piano since you were a child?
When the time period referred to has not finished
I have worked hard this week.
It has rained a lot this year.
We haven't seen her today.
Actions repeated in an unspecified period between the past and now.
They have seen that film six times
It has happened several times already.
She has visited them frequently.
We have eaten at that restaurant many times.
Actions completed in the very recent past (+just)
Have you just finished work?
I have just eaten.
We have just seen her.
Has he just left?
When the precise time of the action is not important or not known
Someone has eaten my soup!
Have you seen 'Gone with the Wind'?
She's studied Japanese, Russian, and English.
Forming the Present Perfect
The present perfect of any verb is composed of two elements : the appropriate form of the auxiliary verb to have (present tense), plus the past participle of the main verb. The past participle of a regular verb is base +ed, e.g. played, arrived, looked. For irregular verbs, see the Table of irregular verbs in the section called 'Verbs'.
|
Affirmative |
||
|
Subject |
to have |
past participle |
|
she |
has |
visited |
|
Negative |
||
|
Subject |
to have + not |
past participle |
|
She |
Hasn’t |
Visited |
|
Interrogative |
||
|
To have |
Subject |
past participle |
|
Has |
she |
Visited ? |
|
Negative interrogative |
||
|
to have + not |
Subject |
past participle |
|
Hasn’t |
she |
visited |
To Walk, present perfect
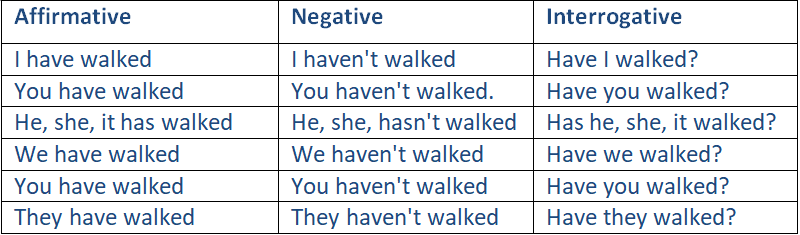
|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|