


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 16-11-2021
Date: 29-12-2021
Date: 3-11-2021
|
Covalent Modification
Many enzymes are regulated by covalent modification, most often by the addition or removal of phosphate groups from specific serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues of the enzyme. Protein phosphorylation is recognized as one of the primary ways in which cellular processes are regulated.
1. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation: Phosphorylation reactions are catalyzed by a family of enzymes called protein kinases that use ATP as the phosphate donor. Phosphate groups are cleaved from phosphorylated enzymes by the action of phosphoprotein phosphatases (Fig. 1).
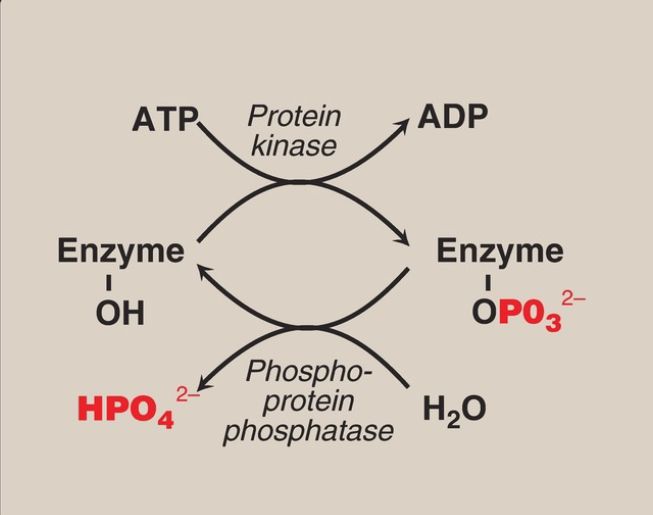
Figure 1: Covalent modification by the addition and removal of phosphate groups. [Note: HPO42− may be represented as Pi and PO32− as P .] ADP =adenosine diphosphate.
2. Enzyme response to phosphorylation: Depending on the specific enzyme, the phosphorylated form may be more or less active than the unphosphorylated enzyme. For example, hormone-mediated phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase (an enzyme that degrades glycogen) increases activity, whereas phosphorylation of glycogen synthase (an enzyme that synthesizes glycogen) decreases activity .



|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقيم ندوة علمية عن روايات كتاب نهج البلاغة
|
|
|