

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Fatty Acid Synthesis (Acetyl CoA carboxylation to malonyl CoA)
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
8-10-2021
6663
Fatty Acid Synthesis (Acetyl CoA carboxylation to malonyl CoA)
The energy for the carbon-to-carbon condensations in fatty acid synthesis is supplied by the carboxylation and then decarboxylation of acyl groups in the cytosol. The carboxylation of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA is catalyzed by acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC) (Fig. 1).
ACC transfers carbon dioxide (CO2) from bicarbonate 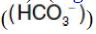 in an ATP-requiring reaction. The coenzyme is biotin (vitamin B7), which is covalently bound to a lysyl residue of the carboxylase . ACC carboxylates the bound biotin, which transfers the activated carboxyl group to acetyl CoA.
in an ATP-requiring reaction. The coenzyme is biotin (vitamin B7), which is covalently bound to a lysyl residue of the carboxylase . ACC carboxylates the bound biotin, which transfers the activated carboxyl group to acetyl CoA.
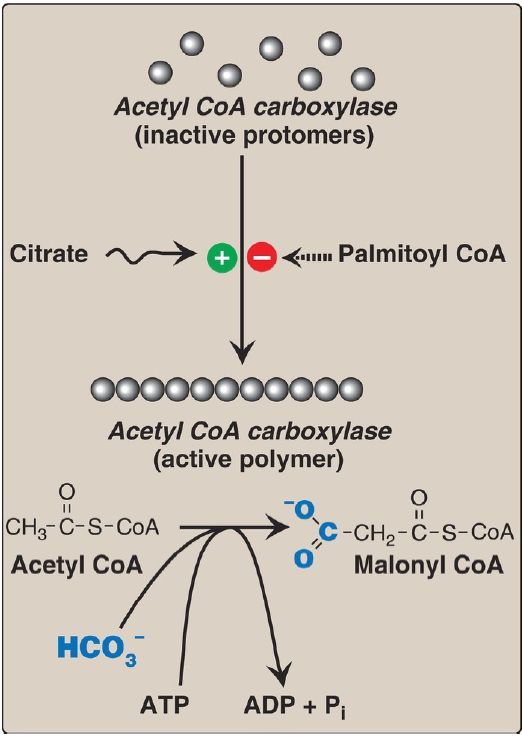
Figure 1: Allosteric regulation of malonyl coenzyme A (CoA) synthesis by acetyl CoA carboxylase. The carboxyl group contributed by bicarbonate 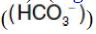 is shown in blue. Pi = inorganic phosphate; ADP = adenosine diphosphate.
is shown in blue. Pi = inorganic phosphate; ADP = adenosine diphosphate.
1. Acetyl CoA carboxylase short-term regulation: This carboxylation is both the rate-limiting and the regulated step in fatty acid synthesis (see Fig. 1). The inactive form of ACC is a protomer (complex of ≥2 polypeptides). The enzyme is allosterically activated by citrate, which causes protomers to polymerize, and allosterically inactivated by palmitoyl CoA (the end product of the pathway), which causes depolymerization. A second mechanism of short-term regulation is by reversible phosphorylation. Adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylates and inactivates ACC. AMPK itself is activated allosterically by AMP and covalently by phosphorylation via several kinases. At least one of these AMPK kinases is activated by cyclic AMP (cAMP)–dependent protein kinase A (PKA). Thus, in the presence of counterregulatory hormones, such as epinephrine and glucagon, ACC is phosphorylated and inactive (Fig. 2). In the presence of insulin, ACC is dephosphorylated and active. [Note: This is analogous to the regulation of glycogen synthase .]
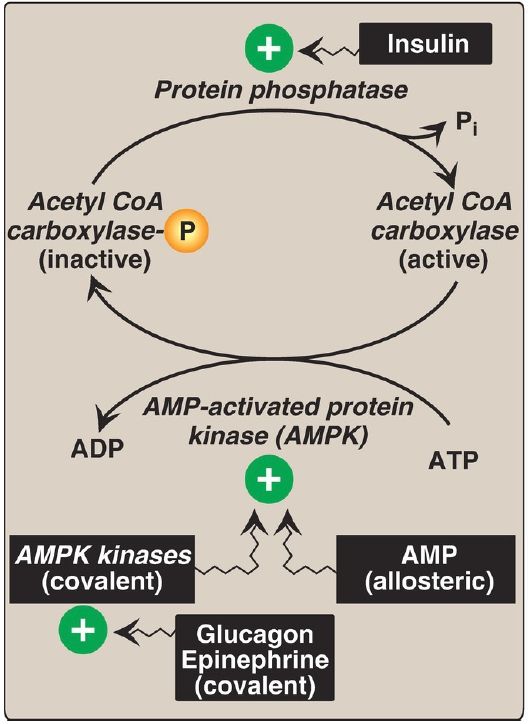
Figure 2: Covalent regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase by AMPK, which itself is regulated both covalently and allosterically. CoA = coenzyme A; ADP and AMP = adenosine di- and monophosphates; = phosphate; Pi = inorganic phosphate.
2. Acetyl CoA carboxylase long-term regulation: Prolonged consumption of a diet containing excess calories (particularly high-carbohydrate, low-fat diets) causes an increase in ACC synthesis, thereby increasing fatty acid synthesis. A low-calorie or a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet has the opposite effect. [Note: ACC synthesis is upregulated by carbohydrate (specifically glucose) via the transcription factor carbohydrate response element–binding protein (ChREBP) and by insulin via the transcription factor sterol regulatory element–binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c). Fatty acid synthase is similarly regulated. Metformin, used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, lowers plasma TAG through activation of AMPK, resulting in inhibition of ACC activity (by phosphorylation) and inhibition of ACC and fatty acid synthase expression (by decreasing SREBP-1c). Metformin lowers blood glucose by increasing AMPKmediated glucose uptake by muscle.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















