


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 28-12-2021
Date: 15-12-2021
Date: 6-12-2021
|
Vitamin E
The E vitamins consist of eight naturally occurring tocopherols, of which α-tocopherol is the most active (Fig. 1). Vitamin E functions as an antioxidant in prevention of nonenzymic oxidations (for example, oxidation of LDL and peroxidation of polyunsaturated FA by O2 and free radicals). [Note: Vitamin C regenerates active vitamin E.]
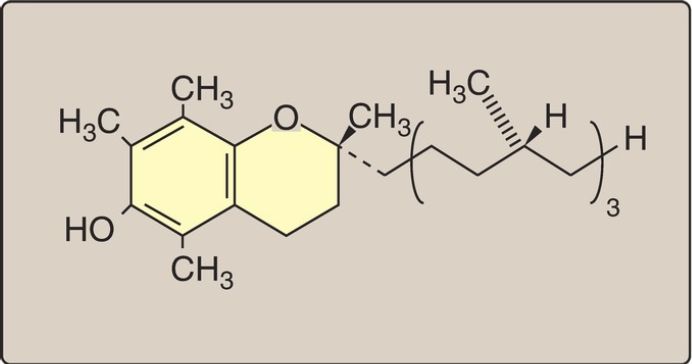
Figure 1: Structure of vitamin E (α-tocopherol).
A. Distribution and requirements
Vegetable oils are rich sources of vitamin E, whereas liver and eggs contain moderate amounts. The RDA for α-tocopherol is 15 mg/day for adults. The vitamin E requirement increases as the intake of polyunsaturated FA increases to limit FA peroxidation.
B. Deficiency
Newborns have low reserves of vitamin E, but breast milk (and formulas) contain the vitamin. Very-low-birth-weight infants may be given supplements to prevent the hemolysis and retinopathy associated with vitamin E deficiency. When observed in adults, deficiency is usually associated with defective lipid absorption or transport. [Note: Abetalipoproteinemia, caused by a defect in the formation of chylomicrons (and VLDL), results in vitamin E deficiency .]
C. Clinical indications for vitamin E
Vitamin E is not recommended for the prevention of chronic disease, such as CVD or cancer. Clinical trials using vitamin E supplementation have been uniformly disappointing. For example, subjects in the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study trial who received high doses of vitamin E not only lacked cardiovascular benefit but also had an increased incidence of stroke. [Note: Vitamins E and C are used to slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration.]
D. Toxicity
Vitamin E is the least toxic of the fat-soluble vitamins, and no toxicity has been observed at doses of 300 mg/day (UL = 1,000 mg/day). Populations consuming diets high in fruits and vegetables show decreased incidence of some chronic diseases. However, clinical trials have failed to show a definitive benefit from supplements of folic acid; vitamins A, C, or E; or antioxidant combinations for the prevention of cancer or CVD.



|
|
|
|
تحذير من "عادة" خلال تنظيف اللسان.. خطيرة على القلب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دراسة علمية تحذر من علاقات حب "اصطناعية" ؟!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تحذّر من خطورة الحرب الثقافية والأخلاقية التي تستهدف المجتمع الإسلاميّ
|
|
|