

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
How Should We Go about Formulating a Reaction Mechanism?
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
23-12-2021
2496
How Should We Go about Formulating a Reaction Mechanism?
Faced with proposing a mechanism for a reaction that involves overall making or breaking of more than two bonds, the beginner almost invariably tries to concoct a process wherein, with a single step, all of the right bonds break and all of the right bonds form. Such mechanisms, called concerted mechanisms, have three disadvantages. First, they are almost impossible to prove correct. Second, prediction of the relative rates of reactions involving concerted mechanisms is especially difficult. Third, concerted mechanisms have a certain sterility in that one has no control over what happens while they are taking place, except an overall control of rate by regulating concentrations, temperature, pressure, choice of solvents, and so on.
To illustrate, suppose that methane chlorination appeared to proceed by way of a one-step concerted mechanism:
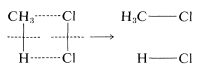
At the instant of reaction, the reactant molecules in effect would disappear into a dark closet and later emerge as product molecules. There is no way to prove experimentally that all of the bonds were made and formed simultaneously. All one could do would be to use the most searching possible tests to probe for the existence of discrete steps. If these tests fail, the reaction still would not be proved concerted because other, still more searching tests might be developed later that would give a different answer. The fact is, once you accept that a particular reaction is concerted, you, in effect, accept the proposition that further work on its mechanism is futile, no matter how important you might feel that other studies would be regarding the factors affecting the reaction rate.
The experienced practitioner in reaction mechanisms accepts a concerted mechanism for a reaction involving the breaking and making of more than two bonds as a last resort. He first will try to analyze the overall transformation in terms of discrete steps that are individually simple enough surely to be concerted and that also involves energetically reasonable intermediates.
Such an analysis of a reaction in terms of discrete mechanistic steps offers many possibilities for experimental studies, especially in development of procedures for detecting the existence, even if highly transitory, of the proposed intermediates. We shall give many examples of the fruitfulness of this kind of approach in subsequent discussions.
Many books and references use ΔF0 instead of ΔG0. The difference between standard Gibbs energy ΔG0 and the Gibbs energy ΔG is that ΔG0 is defined as the value of the free energy when all of the participants are in standard states. The free energy for ΔG for a reaction A+B+⋯⟶X+Y+⋯ is equal to ΔG0−2.303RTlog[X][Y]⋯[A][B]⋯ where the products, [X],[Y]⋯, and the reactants, [A],[B]⋯, do not have to be in standard states.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















