


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-12-18
Date: 2023-08-26
Date: 15-1-2022
|
Morphology
Throughout the preceding chapter, we approached the description of processes involved in word formation as if the unit called the “word” was always a regular and easily identifiable form, even when it is a form such as bambification that we may never have seen before. This doesn’t seem unreasonable when we look at a text of written English, since the “words” in the text are, quite obviously, those sets of things marked in black with the bigger spaces separating them. Unfortunately, there are a number of problems with using this observation as the basis of an attempt to describe language in general, and individual linguistic forms in particular.
In many languages, what appear to be single forms actually turn out to contain a large number of “word-like” elements. For example, in Swahili (spoken throughout East Africa), the form nitakupenda conveys what, in English, would have to be represented as something like I will love you. Now, is the Swahili form a single word? If it is a “word,” then it seems to consist of a number of elements which, in English, turn up as separate “words.” A rough correspondence can be presented in the following way:
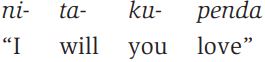
It would seem that this Swahili “word” is rather different from what we think of as an English “word.” Yet, there clearly is some similarity between the languages, in that similar elements of the whole message can be found in both. Perhaps a better way of looking at linguistic forms in different languages would be to use this notion of “elements” in the message, rather than depend on identifying only “words.”
The type of exercise we have just performed is an example of investigating basic forms in language, generally known as morphology. This term, which literally means “the study of forms,” was originally used in biology, but, since the middle of the nineteenth century, has also been used to describe the type of investigation that analyzes all those basic “elements” used in a language. What we have been describing as “elements” in the form of a linguistic message are technically known as “morphemes.”
|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية تستعدّ لتكريم عددٍ من الطالبات المرتديات للعباءة الزينبية في جامعات كركوك
|
|
|