
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Magnification
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 27
2024-03-17
1281
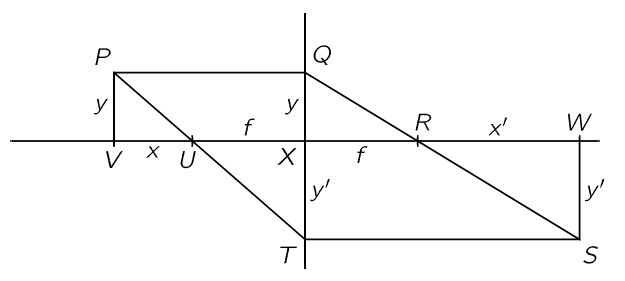
Fig. 27–7. The geometry of imaging by a thin lens.
So far, we have discussed the focusing action only for points on the axis. Now let us discuss also the imaging of objects not exactly on the axis, but a little bit off, so that we can understand the properties of magnification. When we set up a lens so as to focus light from a small filament onto a “point” on a screen, we notice that on the screen we get a “picture” of the same filament, except of a larger or smaller size than the true filament. This must mean that the light comes to a focus from each point of the filament. In order to understand this a little better, let us analyze the thin lens system shown schematically in Fig. 27–7. We know the following facts:
1- Any ray that comes in parallel on one side proceeds toward a certain particular point called the focus on the other side, at a distance f from the lens.
2- Any ray that arrives at the lens from the focus on one side comes out parallel to the axis on the other side.
This is all we need to establish formula (27.12) by geometry, as follows: Suppose we have an object at some distance x from the focus; let the height of the object be y. Then we know that one of the rays, namely PQ, will be bent so as to pass through the focus R on the other side. Now if the lens will focus point P at all, we can find out where if we find out where just one other ray goes, because the new focus will be where the two intersect again. We need only use our ingenuity to find the exact direction of one other ray. But we remember that a parallel ray goes through the focus and vice versa: a ray which goes through the focus will come out parallel! So we draw ray PT through U. (It is true that the actual rays which are doing the focusing may be much more limited than the two we have drawn, but they are harder to figure, so we make believe that we can make this ray.) Since it would come out parallel, we draw TS parallel to XW. The intersection S is the point we need. This will determine the correct place and the correct height. Let us call the height y′ and the distance from the focus, x′. Now we may derive a lens formula. Using the similar triangles PVU and TXU, we find
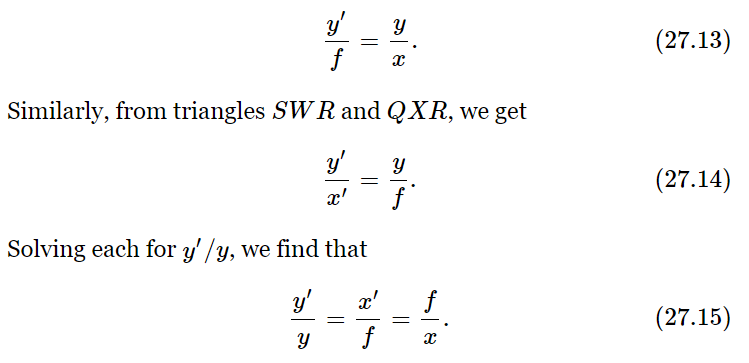
Equation (27.15) is the famous lens formula; in it is everything we need to know about lenses: It tells us the magnification, y′/y, in terms of the distances and the focal lengths. It also connects the two distances x and x′ with f:

which is a much neater form to work with than Eq. (27.12). We leave it to the student to demonstrate that if we call s=x+f and s′=x′+f, Eq. (27.12) is the same as Eq. (27.16).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















