
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Sinusoidal waves
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 29
2024-03-19
1422
First let us fix the position r, and watch the field as a function of time. It is oscillatory at the angular frequency ω. The angular frequency ω can be defined as the rate of change of phase with time (radians per second). We have already studied such a thing, so it should be quite familiar to us by now. The period is the time needed for one oscillation, one complete cycle, and we have worked that out too; it is 2π/ω, because ω times the period is one cycle of the cosine.
Now we introduce a new quantity which is used a great deal in physics. This has to do with the opposite situation, in which we fix t and look at the wave as a function of distance r. Of course we notice that, as a function of r, the wave (29.3) is also oscillatory. That is, aside from 1/r, which we are ignoring, we see that E oscillates as we change the position. So, in analogy with ω, we can define a quantity called the wave number, symbolized as k.
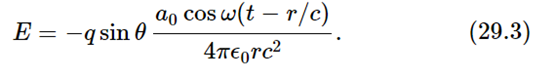
This is defined as the rate of change of phase with distance (radians per meter). That is, as we move in space at a fixed time, the phase changes.
There is another quantity that corresponds to the period, and we might call it the period in space, but it is usually called the wavelength, symbolized λ. The wavelength is the distance occupied by one complete cycle. It is easy to see, then, that the wavelength is 2π/k, because k times the wavelength would be the number of radians that the whole thing changes, being the product of the rate of change of the radians per meter, times the number of meters, and we must make a 2π change for one cycle. So kλ=2π is exactly analogous to ωt0=2π.
Now in our particular wave there is a definite relationship between the frequency and the wavelength, but the above definitions of k and ω are actually quite general. That is, the wavelength and the frequency may not be related in the same way in other physical circumstances. However, in our circumstance the rate of change of phase with distance is easily determined, because if we call ϕ=ω(t−r/c) the phase, and differentiate (partially) with respect to distance r, the rate of change, ∂ϕ/∂r, is
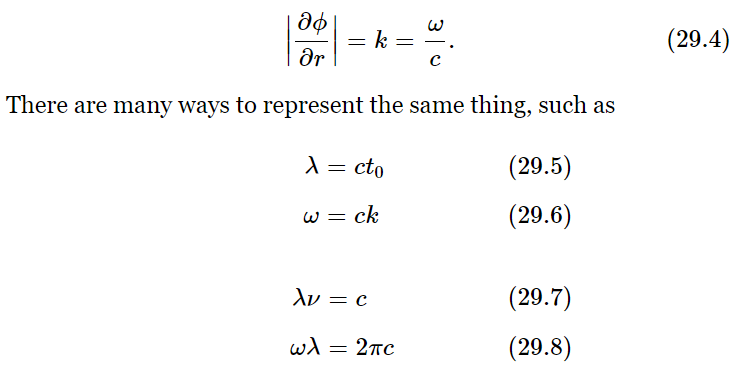
Why is the wavelength equal to c times the period? That’s very easy, of course, because if we sit still and wait for one period to elapse, the waves, travelling at the speed c, will move a distance ct0, and will of course have moved over just one wavelength.
In a physical situation other than that of light, k is not necessarily related to ω in this simple way. If we call the distance along an axis x, then the formula for a cosine wave moving in a direction x with a wave number k and an angular frequency ω will be written in general as cos(ωt−kx).
Now that we have introduced the idea of wavelength, we may say something more about the circumstances in which (29.1) is a legitimate formula. We recall that the field is made up of several pieces, one of which varies inversely as r, another part which varies inversely as r2, and others which vary even faster. It would be worthwhile to know in what circumstances the 1/r part of the field is the most important part, and the other parts are relatively small. Naturally, the answer is “if we go ‘far enough’ away,” because terms which vary inversely as the square ultimately become negligible compared with the 1/r term. How far is “far enough”? The answer is, qualitatively, that the other terms are of order λ/r smaller than the 1/r term. Thus, so long as we are beyond a few wavelengths, (29.1) is an excellent approximation to the field. Sometimes the region beyond a few wavelengths is called the “wave zone.”

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















