


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 24-3-2016
Date: 2025-01-04
Date: 24-3-2016
|
Aminoglycosides are effective mainly in Gram-negative infections and are therefore commonly used in regimens for intra-abdominal infection. Some aminoglycosides, e.g. amikacin, are important components of therapy for MDR-TB. Because they act synergistically with β-lactam anti biotics they are used in combinations to treat biofilm infections, including infective endocarditis and orthopaedic implant infections. They cause very little local irritation at injection sites and negligible allergic responses. Oto- and nephrotoxicity must be avoided by monitoring of renal function and drug levels and by use of short treatment regimens. Aminoglycosides are not subject to an inoculum effect and they all exhibit a post-antibiotic effect. Resistance is mediated mainly through inactivation by aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (AMEs). Plazomicin is a novel aminoglycoside that is not yet inactivated by AMEs.
Pharmacokinetics
- Negligible oral absorption.
- Hydrophilic, so excellent penetration to extracellular fluid in body cavities and serosal fluids, but poor penetration into adipose tissue.
- Very poor intracellular penetration (except hair cells in cochlea and renal cortical cells).
- Negligible CSF and corneal penetration.
- Peak plasma levels 30 minutes after infusion.
- Exhibit a post-antibiotic effect.
- Monitoring of therapeutic levels required.
Gentamicin dosing
- Gentamicin should be dosed according to actual body weight or ideal body weight if obese.
- Except in certain forms of endocarditis, pregnancy, severe burns, end-stage renal disease and paediatric patients, gentamicin can be administered at 7 mg/kg body weight. The appropriate dose interval depends on drug clearance and is determined by reference to the Hartford nomogram (Fig. 1).
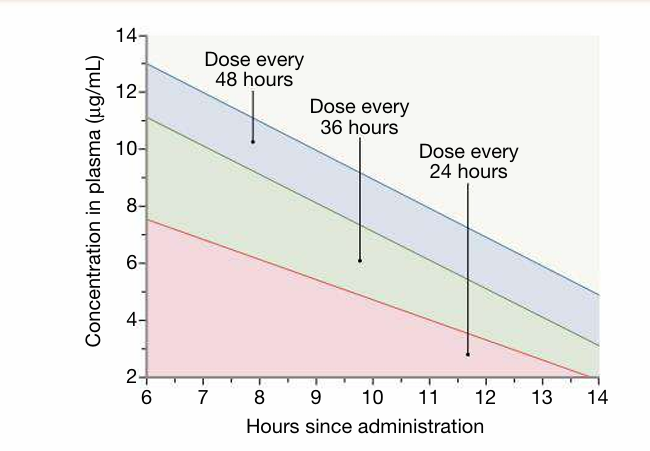
fig1. Dosing of aminoglycosides using the Hartford nomogram. The nomogram is used to determine the dose interval for 7 mg/kg doses of gentamicin or tobramycin, using measurements of drug levels in plasma 6–14 hours after a single dose
- In most other situations, gentamicin is usually administered twice or 3 times daily at 3–5 mg/kg/day with target pre- and post-dose levels of < 1 mg/L and 5–10 mg/L.
Adverse effects
- Renal toxicity (usually reversible) accentuated by other nephrotoxic agents.
- Cochlear toxicity (permanent) more likely in older people and those with a predisposing mitochondrial gene mutation.
- Neuromuscular blockade after rapid intravenous infusion (potentiated by calcium channel blockers, myasthenia gravis and hypomagnesaemia).
Spectinomycin
Chemically similar to the aminoglycosides and given intramuscularly, spectinomycin was developed to treat strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae resistant to β-lactam antibiotics. Unfortunately, resistance to spectinomycin is very common. Its only indication is the treatment of gonococcal urethritis in pregnancy or in patients allergic to β-lactam antibiotics.



|
|
|
|
لشعر لامع وكثيف وصحي.. وصفة تكشف "سرا آسيويا" قديما
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
كيفية الحفاظ على فرامل السيارة لضمان الأمان المثالي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
شعبة مدارس الكفيل: مخيَّم بنات العقيدة يعزِّز القيم الدينية وينمِّي مهارات اتخاذ القرار لدى المتطوِّعات
|
|
|