


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 1-1-2016
Date: 30-12-2015
Date: 1-1-2016
|
Angles of elevation and depression are angles that are formed with the horizontal. If the line of sight is upward from the horizontal, the angle is an angle of elevation; if the line of sight is downward from the horizontal, the angle is an angle of depression. These types of angles and some trigonometry can be used to indirectly calculate heights of objects or distances between points. Alternatively, if the heights or distances are known, the angles can be determined.
Angles of Elevation
Finding a Flagpole’s Height.
Suppose that the height of a flagpole must be determined. The flagpole forms a right angle with level ground. Suppose the flagpole casts a shadow of 20 feet. See part (a) of the figure on the following page. The 20-foot shadow and the flagpole itself form two legs of a right triangle. The triangle’s hypotenuse is formed by the line of sight extending from the end of the shadow (Point E) upwards toward the Sun. The angle of elevation of the Sun has one ray extending along the horizontal toward the bottom of the pole, and the other extending toward the Sun. Furthermore, suppose the angle of elevation measures 50°. Because three parts of this right triangle are known (the right angle, the shadow side, and the angle formed by the shadow and the hypotenuse), there is enough information to find the flagpole’s height.
The relationship between the angle of elevation, the height of the flagpole, and the length of the shadow is represented by the equation tan 50°=b/20, where b represents the height of the flagpole. Solving for b results in b= 20tan 50° ≈ 23.8 feet.
Determining a Building’s Height from Eye Level.
Care is often needed when working with angles of elevation to ensure that the correct measure is being determined. Suppose one wants to determine the height of a building. Perhaps there is no shadow, or perhaps the angle of elevation from a point on the ground cannot be measured. With a type of protractor thatuses gravity, however, the angle of elevation from one’s eye to the top of the building can be measured.
Suppose the angle measured using this type of protractor is 30°, and the horizontal distance to the building is 50 feet. As before, a right triangle is formed. The relationship determined by the given information is tan 30° =x/50. Solving for x results in x= 50tan 30°≈29 feet.
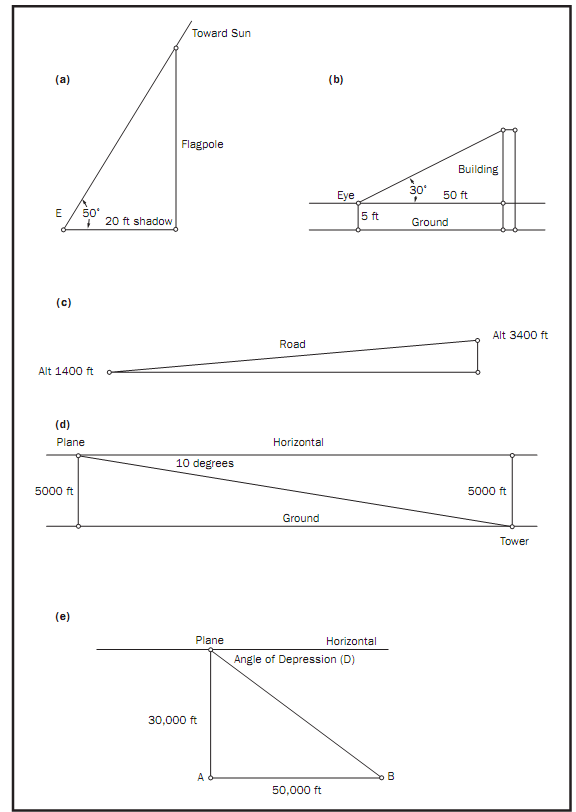
However, when determining the height of the building, the height of one’s eye must be added because the angle was not measured from the ground. See part (b) of the figure. If one’s eye is 5 feet above the ground, the building must be about 34 feet tall.
Calculating a Road’s Angle of Elevation. Using the inverse trigonometric functions, one can also determine the angle of elevation if only the sides of a triangle are known. Suppose a road increases in altitude from 1,400 feet to 3,400 feet over the span of 10 miles (52,800 feet). See part (c) of the figure. The average angle of elevation of the road, called A, can be found by solving the equation tanA =2,000/52,800. To solve for angle A, the inverse tangent of both sides must be taken. This can be denoted as tan-1A. The result is

Angles of Depression
Determining Distance from an Airplane.
Like an angle of elevation, an angle of depression is formed by a ray and the horizontal, but the ray is lower than the horizontal. Suppose that a pilot is flying at an altitude of 5,000 feet and spots a control tower ahead. If the pilot lowers her eyes from the horizontal at an angle of 10°, she can calculate her distance to the tower with right-triangle trigonometry.
See part (d) of the figure. If d represents the direct distance to the tower (measured along the hypotenuse), the pilot can find the distance by solving the equation sin 10° = 5,000/d, which yields a solution of approximately28,800 feet, or close to 5 1/2 miles.
Similarly, the pilot can also determine the horizontal difference (the distance along the ground) between her current position and the tower.
If g represents the horizontal difference, she solves the equation tan 10° =5,000/g, which yields a solution of approximately 28,400 feet, or a little less than 5 1/2 miles. With such a small angle, the difference between the horizontal leg and the hypotenuse is small.
Finding an Angle of Depression. As with angles of elevation, if two of the sides of the right triangle are known, one can solve for an angle of depression. For example, suppose a plane is flying at an altitude of 30,000 feet directly above point A on the ground. Furthermore, suppose that point A is 50,000 feet from another point on the ground, point B. See part (e) of the figure. Note that the angle of depression from the plane (D) is congruent to the angle of elevation from point B.
The equation tan
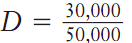
can be used to determine the angle of depression, D, from the plane to point B. To do so, the inverse tangent of
both sides is taken, resulting in
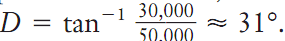
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Reference
Alvarez, Richard. “How High Is the Water Tower?” Mathematics Teacher 89, no. 4(1996):274–278.
Sovchik, Robert, and L. J. Meconi. “Ideas: Classroom Activities for Mathematics: Clinometer Inclines.” Arithmetic Teacher 41, no. 5 (1994):253–262.

|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|