
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
BLACKBODIES AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
الجزء والصفحة:
p15
7-3-2016
3308
BLACKBODIES AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES
To get an idea of how blackbody radiation depends on temperature, consider blackbody radiation curves for an object at various temperatures, as shown in Figure 1.1. Consider first an extremely hot object at 6000 K. Although a great deal of radiation is emitted in the infrared region of the spectrum, the vast majority
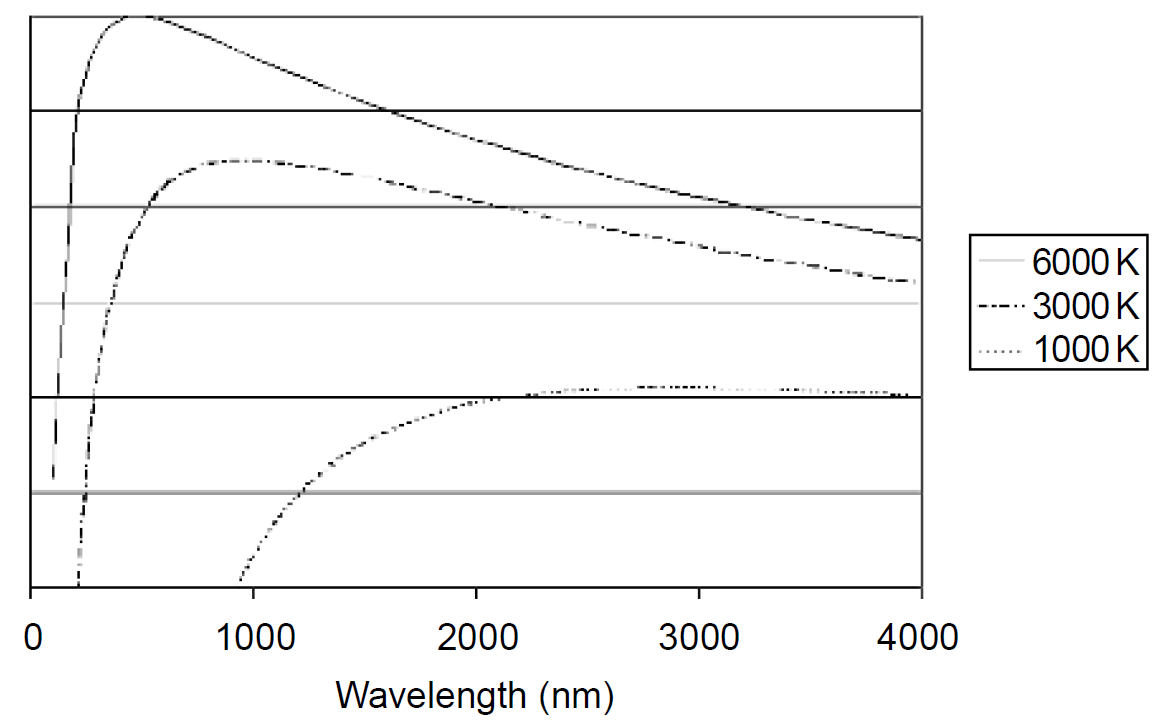
Figure 1.1. Blackbody radiation spectra.
lies in the visible range and more specifically, in the blue region of the visible spectrum. Such an object is said to have a color temperature of 6000 K and approximates that produced by sunlight. Many commercial lamps, especially those used by photographers, have a color temperature rating like this; it is simply a comparison to an equivalent output from a blackbody radiator. Considering a somewhat cooler object at 3000 K, the object appears red when viewed since there is a great deal more red light emitted than blue light. Incandescent lamps often have a color temperature around 3500 K, and photographs taken under such light appear reddish yellow and require a blue correcting filter to have accurate color reproduction. This point is also illustrated in the differences between light from a regular incandescent lamp and a halogen lamp. In halogen lamps the filament burns in an atmosphere of halogen gas (e.g., iodine) which allows the filament to burn much hotter than in an ordinary incandescent light bulb without burning out prematurely. The increased temperature results in a shift from the reddish-yellow (warmer) light of an ordinary incandescent lamp to a much whiter light (i.e., containing more blue). Halogen lighting is therefore often used for illumination of objects where truer color rendition is required (e.g., display of artwork). As this object cools to, say, 1000 K, the emission of light shifts even further into the infrared, and only a small amount of red light is emitted (with almost no blue). Such an object is said to be “red hot” and the vast majority of its emission is in the infrared region between 2- and 6-μm wavelengths. The red we see is only a tiny fraction of the total radiation emitted. Objects at room temperature (300 K) also emit radiation in the infrared centered at about 10 μm. In fact, even objects at a cold 3 K (the background temperature of the universe found in deep outer space) emit radiation at 3-μm wavelengths. Such long wavelengths are in the microwave region of the spectrum and can be detected using sensitive microwave receivers. Cosmologists often call this microwave background the “leftovers” from the “big bang” that created the universe.
 الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















