


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 4-9-2016
Date: 6-9-2016
Date: 9-8-2016
|
Spin-Dependent Potentials
Consider the nonrelativistic scattering of an electron of mass and momentum k through an angle θ. Calculate the differential cross section in the Born approximation for the spin-dependent potential
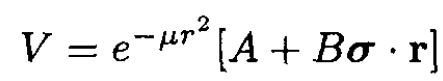 (i)
(i)
where σ = (σx, σy, σz) are the Pauli spin matrices and (μ, A, B) are constants. Assume the initial spin is polarized along the incident direction, and sum over all final spins. (Note: Ignore that the potential violates parity.)
SOLUTION
In the first Born approximation the scattering is proportional to the square of the matrix element between initial and final states. If the initial wave vector is k and the final one is k', set q = k' – k and evaluate
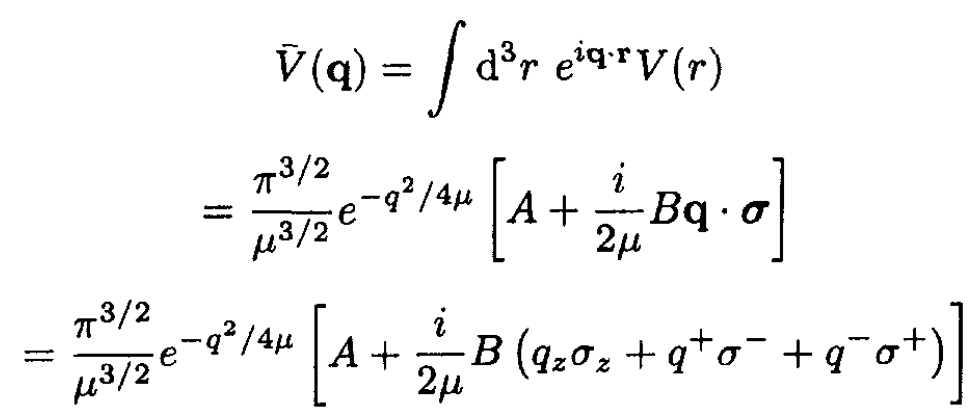 (1)
(1)
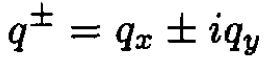 (2)
(2)
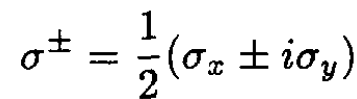 (3)
(3)
where we have written the transverse components of momentum in terms of spin raising and lowering operators. The initial spin is pointing along the direction of the initial wave vector k, which we define as the z-direction Let us quantize the final spins along the same axis. Now consider how the three factors scatter the spins:
a) The term A is spin independent. It puts the final spin in the same state as the initial spin.
b) Bqzσz is a diagonal operator, so the final spin is also along the initial direction, and this term has a value of Bqz.
c) Bq+σ - flips the spin from to and contributes a matrix element of Bq+ to the final state with the spin reversed.
d) Bq-σ+ gives a matrix element of zero since the initial spin cannot be raised.
When we take the magnitude squared of each transition and sum over final states, we get the factors for spins of
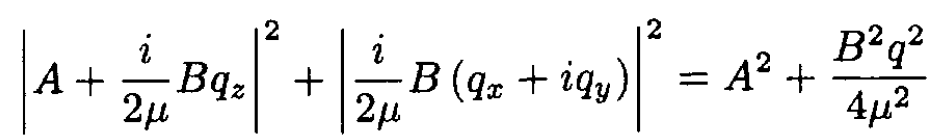 (4)
(4)
The differential cross section is written as
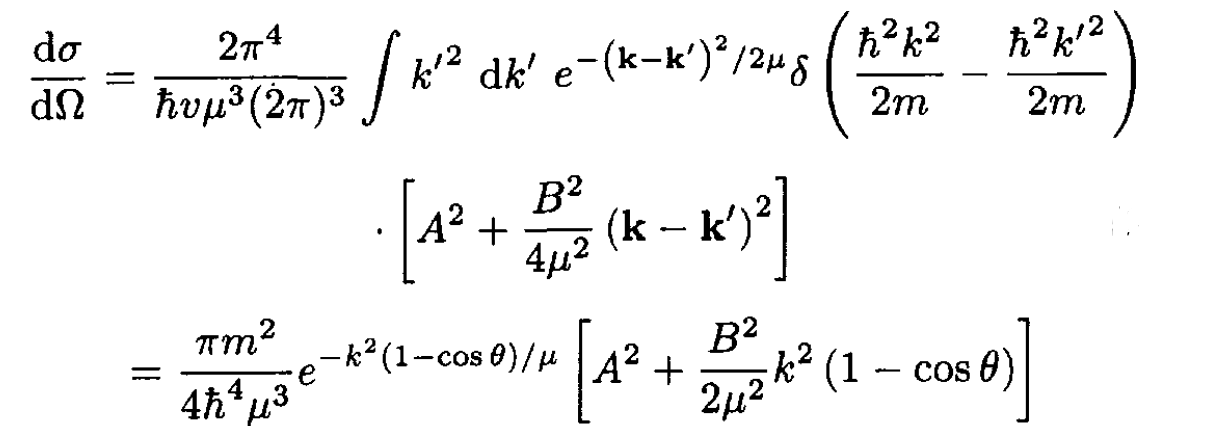 (5)
(5)
We have used the fact that energy is conserved, so |k'| = |k|, to set (k' – k)2 = 2k2(1 – cos θ).



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|