


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 24-11-2016
Date: 10-10-2016
Date: 18-10-2016
|
Ferromagnetism
Why are so few substances ferromagnetic, yet practically all materials exhibit paramagnetic behavior?
Answer
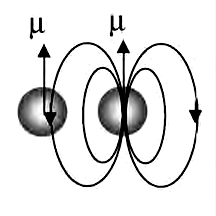
Many atoms and molecules have an inherent magnetic dipole moment. When we assume that each dipole behaves independently of its neighbors except for its alignment, the magnetic field direction next to the dipole is opposite to the direction in which the dipole itself points. In paramagnetic substances the dipoles are far enough apart to behave approximately independently, and when no applied field is present, these dipoles have random orientations. Each dipole is affected by the applied magnetic field but not by its neighbors. The applied magnetic field competes with the random thermal motion to cause a net magnetization that increases nearly linearly with the strength of the applied field, the ratio being known as the magnetic susceptibility.
When the density of magnetic dipoles becomes high enough for neighbors to affect each other, only neighbors in the head-to-tail configuration will tend to align one another. The side-by-side neighbors will be oppositely aligned because all the fields from its neighbors are opposite at its location. Thus every other dipole in each layer of the crystal will be aligned and form one sub lattice, like the white squares on a checkerboard, and the remaining dipoles (on the black squares) will form a second sub lattice of dipoles pointing in the opposite direction. The two sublattices interact strongly or ferromagnettically, but they cancel each other’s magnetization. Therefore, when magnetic dipole moments are crowded together, they are more likely to disalign their nearest neighbors than to align them. So ferromagnetism is rare.
Then how can ferromagnetic substances exist at all? Via a cooperative effect when the dipoles are very close and no longer behave independently. In these conditions a state of lower energy can form if groups of dipoles align each other into magnetic domains that themselves point in random directions. With an applied field, these domains will change their sizes to find the lowest energy state. Of course, domain formation cannot form above a certain temperature called the Curie temperature, because the thermal agitation interferes with the dipole interactions. Above the Curie temperature the substance becomes paramagnetic.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|