


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 12-1-2017
Date: 9-1-2017
Date: 9-1-2017
|
In this section we will investigate the rules by which sets may be combined to form new sets. First, for arbitrary sets X and Y, the union of X and Y is defined to be the set consisting of all elements which are either in X or in Y or in both X and Y. This new set is denoted by X + Y. In the illustration of Section (Element and set) for example, R + Y is the set of all red and all yellow books, Y + E + G is the universal set of all books in the stack, and R + E is just B, the set of all books written in English.
Next, the intersection of X and Y, for arbitrary sets X and Y, is defined to be the set consisting of those elements which are both in X and in Y.
The intersection of X and Y will be denoted by XY, or by X .Y We will refer to the centered dot(.) whenever it is desired to discuss the process of forming an intersection, just as the symbol (+) will refer to the process of forming the union of sets. For convenience the centered dot is usually omitted in algebraic expressions, as is common in the algebra of numbers.
Again referring to the example of Section (Element and set), we note that EB is the set of black books written in English, RY is the null set, and RE is R, the set of red books.
As immediate consequences of the definitions of (+)(.), and ('), we note that for an arbitrary set X, X + X' = 1 and XX' = 0. The following theorem also comes directly from these definitions.
THEOREM. If m is any element in the universal set and X and Y are arbitrary sets, then m is a member of one and only one of the sets X Y, XY', X'Y, and X'Y'.
Proof. By the definition of complement, m is an element of either X or X' but not both. If it happens that m e X, then since m is an element of either Y or Y' but not both, m is a member of X Y or X' Y' but not both, by definition of intersection. Similarly, if m is a member of X', then m is a member of X'Y or X'Y' but not both, which completes the proof.
The operations just defined are not independent of the symbols and relations defined in Section (Element and set). A little reflection will reveal that the five conditions X ⊆ Y, XY = X, X + Y = Y, XY' = 0, and X' + Y = 1 all represent the same condition on the sets X and Y, namely, that each element of the set X is a member of the set Y. Again, the set X + Y may be written (X'Y')'. These relationships simply illustrate the fact that we have introduced more symbols than are really necessary to treat the algebra of sets. The significance of this fact will be examined more closely in a later section. In the meantime, we will find it convenient to use all these symbols.
The symbols used in this chapter for intersection, union, and complementation are by no means standard. It was considered desirable to use a single notation throughout the text for the several applications of Boolean algebra. The set chosen is the one most commonly used in the application to circuit algebra. The notations most commonly used in other books are listed in the following table.
SYMBOLS IN COMMON USAGE
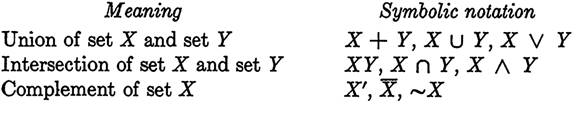

|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|