
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Electric Potential and Electric Field
المؤلف:
المؤسسة العامة للتعليم الفني والتدريب المهني
المصدر:
مقدمة عن علم الكهربية الساكنة
الجزء والصفحة:
...
16-2-2017
2974
Electric Potential and Electric Field
Simple Case (Uniform electric field):
The potential difference between two points A and B in a Uniform electric field E can be found as follow, Assume that a positive test charge qo is moved by an external agent from A to B in uniform electric field as shown in figure 1.1.
The test charge qo is affected by electric force of qoE in the downward direction. To move the charge from A to B an external force F of the same magnitude to the electric force but in the opposite direction. The work W done by the external agent is:

WAB = Fd = qoEd
The potential difference VB-VA is
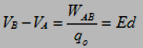
This equation shows the relation between the potential difference and the electric field for a special case (uniform electric field). Note that E has a new unit (V/m). hence,
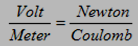
The relation in general case (not uniform electric field):
If the test charge qo is moved along a curved path from A to B as shown in figure 1.2. The electric field exerts a force qoE on the charge. To keep the charge moving without accelerating, an external agent must apply a force F equal to -qoE.
If the test charge moves distance dl along the path from A to B, the work done is F.dl. The total work is given by,
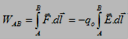
The potential difference VB-VA is,
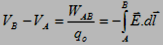
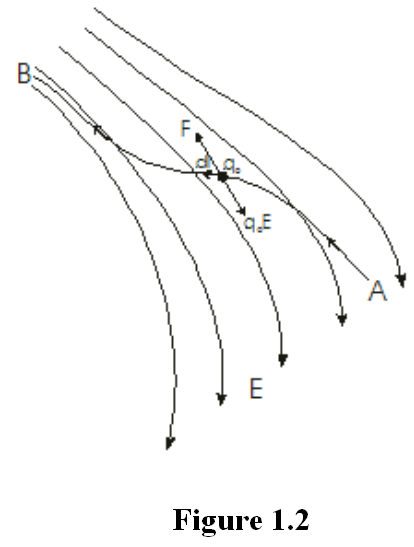
وتكون الزاوية dl هي التي تحدد المسار ومنه اتجاه متجه الإزاحة B الى A لاحظ هنا أن حدود التكامل من ومتجه المجال الكهربي هي الزاوية المحصورة بين منتجه الإزاحة θ.
If the point A is taken to infinity then VA=0 the potential V at point B is,
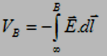
This equation gives the general relation between the potential and the electric field.
Example 1.1
Derive the potential difference between points A and B in uniform electric field using the general case.
Solution
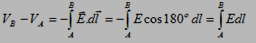
E is uniform (constant) and the integration over the path A to B is d, therefore
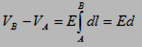
The Electron Volt Unit
A widely used unit of energy in atomic physics is the electron volt (eV).
ELECTRON VOLT, unit of energy, used by physicists to express the energy of ions and subatomic particles that have been accelerated in particle accelerators. One electron volt is equal to the amount of energy gained by an electron traveling through an electrical potential difference of 1 V; this is equivalent to 1.60207 x 10–19J. Electron volts are commonly expressed as million electron volts (MeV) and billion electron volts (BeV or GeV).
Assume two points A and B near to a positive charge q as shown in figure 1.3. To calculate the potential difference VB-VA we assume a test charge qo is moved without acceleration from A to B.
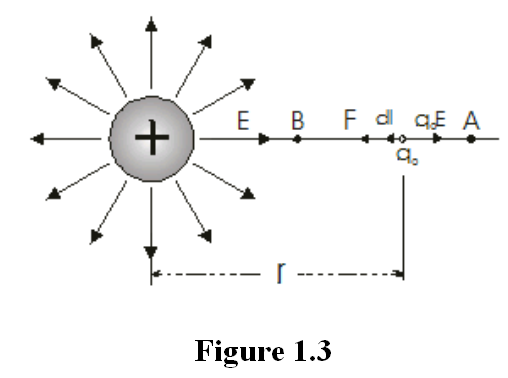
In the figure above the electric field E is directed to the right and dl to the left.

However when we move a distance dl to the left, we are moving in a direction of decreasing r. Thus

Therefore
-Edl = Edr
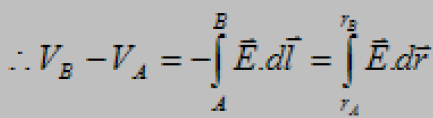
Substitute for E
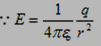
We get
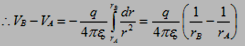
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















