


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 14-3-2017
Date: 12-3-2017
Date: 12-3-2017
|
Angles around a point will always add up to 360 degrees.

The angles above all add to 360°
53° + 80° + 140° + 87° = 360°
Because of this, we can find an unknown angle.
|
|
Example: What is angle "c"? To find angle c we take the sum of the known angles and take that from 360° Sum of known angles = 110° + 75° + 50° + 63° Angle c = 360° − 298° |
Angles On One Side of A Straight Line
Angles on one side of a straight line will always add to 180 degrees.
If a line is split into 2 and you know one angle you can always find the other one.
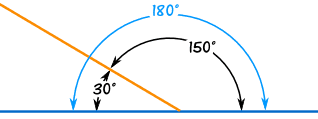
30° + 150° = 180°
Example: If we know one angle is 45° what is angle "a" ?
|
|
Angle a is 180° − 45° = 135° |
This method can be used for several angles on one side of a straight line.
Example: What is angle "b" ?
|
|
Angle b is 180° less the sum of the other angles. Sum of known angles = 45° + 39° + 24° Angle b = 180° − 108° |
Interior Angle
An Interior Angle is an angle inside a shape.
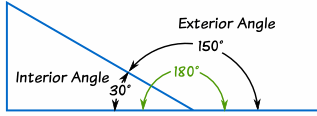
Exterior Angle
The Exterior Angle is the angle between any side of a shape, and a line extended from the next side.

Interior Angles of Polygons
An Interior Angle is an angle inside a shape.

Triangles
The Interior Angles of a Triangle add up to 180°
|
|
|
|
90° + 60° + 30° = 180° |
80° + 70° + 30° = 180° |
|
It works for this triangle! |
Let's tilt a line by 10° ... It still works, because one angle went up by 10°, but the other went down by 10° |
Quadrilaterals (Squares, etc)
(A Quadrilateral has 4 straight sides)
|
|
|
|
90° + 90° + 90° + 90° = 360° |
80° + 100° + 90° + 90° = 360° |
|
A Square adds up to 360° |
Let's tilt a line by 10° ... still adds up to 360°! |
|
The Interior Angles of a Quadrilateral add up to 360° |
|
Because there are Two Triangles in a Square
|
The interior angles in this triangle add up to 180° |
|
... and for this square they add up to 360° ... because the square can be made from two triangles! |
Pentagon
|
|
|
A pentagon has 5 sides, and can be made from three triangles, so you know what ... ... its interior angles add up to 3 × 180° = 540° And if it is a regular pentagon (all angles the same), then each angle is 540° / 5 = 108° (Exercise: make sure each triangle here adds up to 180°, and check that the pentagon's interior angles add up to 540°) |
|
|
The Interior Angles of a Pentagon add up to 540° |
|
The General Rule
Each time we add a side (triangle to quadrilateral, quadrilateral to pentagon, etc), we add another 180° to the total:
|
|
|
|
If it is a Regular Polygon (all sides are equal, all angles are equal) |
|
|
Shape |
Sides |
Sum of |
Shape |
Each Angle |
|
Triangle |
3 |
180° |
|
60° |
|
Quadrilateral |
4 |
360° |
|
90° |
|
Pentagon |
5 |
540° |
|
108° |
|
Hexagon |
6 |
720° |
|
120° |
|
Heptagon (or Septagon) |
7 |
900° |
|
128.57...° |
|
Octagon |
8 |
1080° |
|
135° |
|
Nonagon |
9 |
1260° |
|
140° |
|
... |
... |
.. |
... |
... |
|
Any Polygon |
n |
(n-2) × 180° |
|
(n-2) × 180° / n |
So the general rule is:
Sum of Interior Angles = (n-2) × 180°
Each Angle (of a Regular Polygon) = (n-2) × 180° / n
Perhaps an example will help:
Example: What about a Regular Decagon (10 sides) ?
|
|
And it is a Regular Decagon so: Each interior angle = 1440°/10 = 144° |
Exterior Angles of Polygons
The Exterior Angle is the angle between any side of a shape,
and a line extended from the next side.
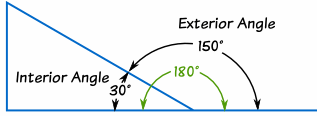
Note: when you add up the Interior Angle and Exterior Angle you get a straight line, 180°.
Polygons
A Polygon is any flat shape with straight sides
|
The Exterior Angles of a Polygon add up to 360° |
||
|
|
In other words the exterior angles add up to one full revolution (Exercise: try this with a square, then with some interesting polygon you invent yourself.)
|
|
|
Here is another way to think about it: |
|

|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|