


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 8-1-2017
Date: 22-11-2020
Date: 1-7-2017
|
Freezing Point Depression
When a solution freezes, the solid is usually pure solvent. Thus the solid-vapor equilibrium (sublimation) P-T curve is unaffected by the presence of solute. The intersection of this curve and the liquid-vapor curve is the triple point (nearly the same temperature as the freezing point, which is measured at atmospheric pressure). Since a solute lowers the solvent vapor pressure, the triple point is shifted to lower temperature, as shown in Figure 1.1. Detailed calculations show that the decrease in freezing point for a dilute solution is proportional to the total molal concentration of solutes
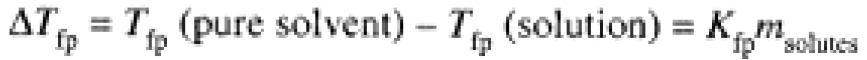
Kfp is the molal freezing-point constant of the solvent. Like Kbp, Kfp is a property of the solvent, independent of the nature of the solutes.
Example
The freezing point of pure camphor is 178.4°C and Kfp = 40.0 K kg/mol. Find the freezing point of a solution containing 1.50 g of a compound of molar mass 125 g/mol in 35.0 g of camphor. The molality of the solution is
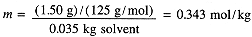
Thus
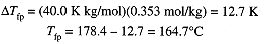
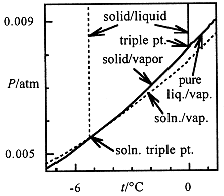
Figure 1.1. Solid-liquid, solid-vapor and liquid-vapor equilibrium curves for pure water (solid curves) and for a solution (dashed curves). The triple point (where solid, liquid, and vapor coexist and at nearly the same temperature as the freezing point) is shifted to lower temperature for the solution.



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|