


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-8-2017
Date: 16-8-2017
Date: 18-9-2017
|
Ethanolamines
A mixture of mono-, di-, and triethanolamines is obtained by the reaction between ethylene oxide (EO) and aqueous ammonia. The reaction conditions are approximately 30–40°C and atmospheric pressure:
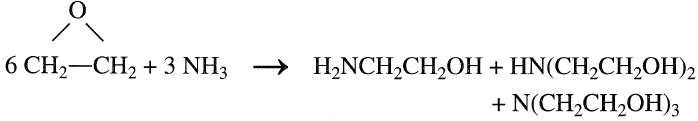
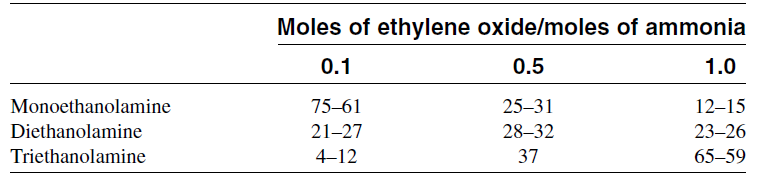
The relative ratios of the ethanolamines produced depend principally on the ethylene oxide/ammonia ratio. A low EO/NH3 ratio increases monoethanolamine yield. Increasing this ratio increases the yield of di-and triethanolamines. Table 1.1 shows the weight ratios of ethanolamines as a function of the mole ratios of the reactants. Ethanolamines are important absorbents of acid gases in natural gas treatment processes. Another major use of ethanolamines is the production of surfactants. The reaction between ethanolamines and fatty acids
Table 1.1: Weight ratios of ethanolamines as a function of the mole ratios of the reactants
produces ethanolamides. For example, when lauric acid and monoethanolamine are used, N-(2hydroxyethyl)-lauramide is obtained:
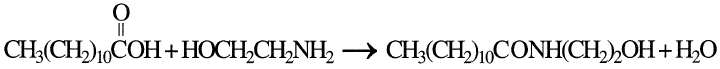
Lauric acid is the main fatty acid used for producing ethanolamides. Monoethanolamides are used primarily in heavy-duty powder detergents as foam stabilizers and rinse improvers.



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|