
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Absorption of Pump Radiation by the Gain Medium and Transfer of Energy to the Upper Laser Level
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner Michael Bass
المصدر:
Solid-state Lasers
الجزء والصفحة:
90
31-1-2021
2538
Absorption of Pump Radiation by the Gain Medium and Transfer of Energy to the Upper Laser Level
This energy transfer can be divided into two processes. The first is the absorption of pump radiation into the pump bands of the gain medium expressed by ηa, and the second is the transfer of energy from the pump band to the upper laser level expressed by ηQηs.
The absorption efficiency is the ratio of power Pa absorbed to power Pe entering the laser medium
ηa = Pa/Pe. ........(1)
The quantity ηa is a function of the path length and the spectral absorption coefficient of the laser medium integrated over the emission spectrum of the pump source. If the pump radiation is totally diffuse inside the laser rod, as is the case when the lateral surface is rough ground, a good approximation can be derived by expressing (1) in a different form
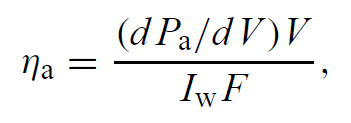 .......(2)
.......(2)
where dPa/dV is the power absorbed per volume, Iw is the power density at the cylindrical surface of the rod, and F, V are the cylindrical rod surface and volume of the rod, respectively.
The power absorbed per volume can also be expressed by dPa/dV = α0 Iav, where α0 is the absorption coefficient of the laser material averaged over the spectral emission range of the lamp and Iav is the average power density inside the rod. Radiation with an energy density Wav propagating at a velocity c has a power density of Iav = cWav, where c = c0/n0 is the speed of light in the medium and n0 is the refractive index. The energy density in the laser rod has a radial dependence due to absorption. The average value Wav can be closely approximated by taking the energy density Ws at the surface weighted by the factor exp(−α0R), where R is the rod radius and α0 is the absorption coefficient. It follows that this is a valid approximation over a large range of α0. From these considerations follows
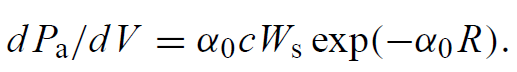 ...(3)
...(3)
Owing to grinding the lateral surface of the rod, the pump radiation upon entering the rod will be diffused. For an enclosure with diffusely reflecting walls, we obtain from blackbody radiation theory a relationship between energy Ws inside the enclosure and the intensity Iw emitted by the walls
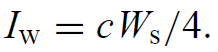 .......(4)
.......(4)
Introducing (3, 4) into (2) yields our final result
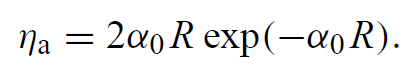 ......(5)
......(5)
For diode pumped lasers, the absorption efficiency can be approximated by
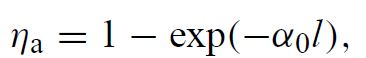 .....(5)
.....(5)
where α0 is the absorption coefficient of the laser crystal at the wavelength emitted by the laser diode and l is the path length in the crystal. Detailed data on ηa for both flashlamp.
The upper state efficiency may be defined as the ratio of the power emitted at the laser transition to the power absorbed into the pump bands. This efficiency is the product of two contributing factors, the quantum efficiency ηQ, which is defined as the number of photons contributing to laser emission divided by the number of pump photons, and ηS, the quantum defect efficiency. The latter is sometimes referred to as the Stokes factor, which represents the ratio of the photon energy emitted at the laser transition hνL to the energy of a pump photon hνp, that is,
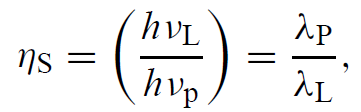 ..........(6)
..........(6)
where λP and λL is the wavelength of the pump transition and the laser wavelength, respectively. For Nd :YAG emitting at 1064 nm that is pumped by a laser diode array at 808 nm, we obtain ηS = 0.76, and ηQ = 0.90.
In a flashlamp-pumped system, the value of ηS is an average value derived from considering the whole absorption spectrum of the laser.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















