

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
Functions
المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
المصدر:
www.almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
...
6-3-2017
1274
What is a function?
A function is a set of mathematical operations performed on one or more inputs (variables) that results in an output. For now, functions will take one or more real numbers as an input, and return a numerical output. In more advanced classes you'll learn about far more complex functions! However, a simple function might return the input plus one. Such a function would look like:
Y = X + 1
In this case, X in the input value, and Y is the output. By putting any number in for X, we calculate a corresponding output Y by simply adding one. The set of possible input values is known as the domain, while the set of possible outputs is known as the range.
Here are two more examples of what functions look like:
1) y = 3x - 2
2) h = 5x + 4y
Let's examine the first example:
In the function, y = 3x - 2, the variable y represents the function of whatever inputs appear on the other side of the equation. In other words, y is a function of the variable x in y = 3x - 2. Because of that, we sometimes see the function written in this form:
f(x) = 3x - 2
What does f(x) mean?
That means just the same as y= in front of an equation. Since there's really no significance to y, and it's just an arbitrary letter that represents the output of the function, sometimes it will be written as f(x) to indicate the the expression is a function of x. Note that you'll also see it written as g(x), h(x), and so forth, but f(x) is the most common because function starts with the letter f.
What does it mean to evaluate a function?
To evaluate a function means to pick different values for the input (often named x) in order to find the output (often named y). In terms of evaluation, for every choice of x that you pick, only onecorresponding value of y will be the end result. You'll often be directed to evaluate a particular function for a certain value of x. That means just plug in that value for x and see what you get, like below:
Evaluate for x=2:
y = 4*x - 7
Solution:
We have our function already solved for y, and we need to just plug in x=2 to evaluate the function at that point.
y = 4*2 - 7
y = 8 - 7
y = 1
Can there be more than one possible answer?
No. A function is a unique mapping from the domain (the inputs) to the range (the outputs). There can only be one output for any input. There can, however, be many inputs which give the same output (consider y=4+0*x).
What is a one-to-one function?
A one-to-one function has a stricter definition than a regular function. Not only does each input map to one and only one output, but each output maps back to one and only one input.
What is the difference between independent and dependent variables?
Independent variables are the inputs -- we can pick them, so they're independent of the function itself. Dependent variables are the outputs -- they depend on the function and your selection of the inputs (independent variables).
Often these terms can be difficult to understand in the context of a simple math equation, like y=2x. Afterall, we could solve the equation for x and call it the dependent variable if we wished. That's because it's a one-to-one function. However, the terminology may make more sense when viewed as part of a larger problem, especially one involving physical quantities. For instance, if we're calculating the price of a tank of gas, the total price would be dependent on the number of gallons purchased, which is independently chosen by the driver.
Just remember that the independent variable is the one you choose (the input) -- the dependentvariable is the result of the function (the output, or the answer).
More complicated functions
Not everything will look like y=4x or f(x) = 3 - x
What about polynomial functions? Polynomial functions are functions that can be written when combining coefficients, variables and exponents. Look over these polynomial functions:
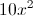
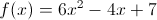
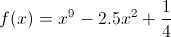
Each of the above is a function. Even the first example, which doesn't have a y= or a f(x) can be considered a function -- it has an input value (x) and an output value (the answer you get when you evaluate it for a particular x). They each have independent and dependent variables, and they each have a domain and range.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















