

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
Point Slope Form
المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
المصدر:
www.almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
...
8-3-2017
2012
Point-slope refers to a method for graphing a linear equation on an x-y axis. When graphing a linear equation, the whole idea is to take pairs of x's and y's and plot them on the graph. While you could plot several points by just plugging in values of x, the point-slope form makes the whole process simpler. Point-slope form is also used to take a graph and find the equation of that particular line.
The point slope form gets its name because it uses a single point on the graph and the slope of the line. Think about it this way: You have a starting point on a map, and you are given a direction to head. You have all the information you need to draw a single line on the map.
The standard point-slope equation looks like this:
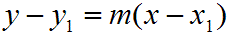
It should be noted that "y1" does not mean y multipled by 1. In this case it simply denotes a particular y value which you will plug into the equation. The variable m is the slope of the line.
Example 1
You are given the point (4,3) and a slope of 2. Find the equation for this line in point slope form.
Solution:
Just plug the given values into your point-slope formula above. Your point (4,3) is in the form of (x1,y1). That means where you see y1, use 3. Where you see x1, use 4. Your slope was given to you, so where you see m, use 2. Pretty simple, huh? Your final result should look like:
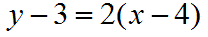
More Practice:
Your point is (-1,5). The slope is 1/2. Create the equation that describes this line in point-slope form. Try working it out on your own. The answer is: 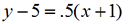 .
.
If that's not what you got, re-read the lesson and try again.
Point-slope form is all about having a single point and a direction (slope) and converting that between an algebraic equation and a graph. In the example above, we took a given set of point and slope and made an equation. Now let's take an equation and find out the point and slope so we can graph it.
Example 2
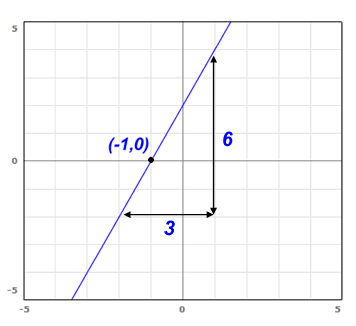
Find the equation (in point-slope form) for the line shown in this graph:
Solution:
To write the equation, we need two things: a point, and a slope. It is simple to find a point because we just need ANY point on the line. The point I've indicated, (-1,0), just happens to be the easiest one to find. Note also that it is useful to pick a point on the axis, because one of the values will be zero.
Finding the slope requires a little calculation, but it is also pretty easy. Just count the number of lines on the graph paper going in each direction of a triangle, like I've shown. Remember that slope is rise over run, or y/x. Therefore the slope of this line is 2. You could have used any triangle to figure out the slope and you would still get the same answer.
Putting it all together, our point is (-1,0) and our slope is 2. We know how to use the point-slope form, so the final answer is:
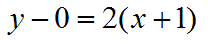
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















