

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Half-Reaction Method
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 86
13-7-2017
1068
Half-Reaction Method:
1. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions, adding electrons (e-) on the right side of the oxidation half-reaction and on the left side of the reduction half reaction to balance the changes in ON.
2. By inspection balance the half-reactions, adding H2O(l), H+(aq) or OH-(aq) as required. Adjust the coefficients in the two half-reactions so that the numbers of electrons are equal in each, and add the two half-reactions (the electrons cancel).
3. For either method, check the final equation to make sure that atoms and charge are balanced.
The rules by themselves are no doubt confusing. Let's see how they work with some examples.
Example 1
Balance the oxidation-reduction equation for the oxidation of H2S(aq) by HNO3(aq) to produce NO(g) and S(s) in aqueous acidic solution (thus H+ and H2O may be involved).
(1) 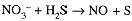
(2) In NO3-, ON(N) = +5; in NO, ON(N) = +2, ΔON = -3. In H2S, ON(S) = -2; in S, ON(S) = 0, ΔON = +2.
ON Method:
(3') Multiply the coefficients of N-containing species by 2 to get a 6-electron overall reduction; multiply the coefficients of S-containing species by 3 to get a 6 electron overall oxidation:
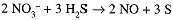
(4') Balance O by adding 4 H2O to the right; then balance H by adding 2 H+ to the left:
2 H+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 3 H2S(aq) → 2 NO(g) + 3 S(s) + 4 H2O(l)
Half-Reaction Method:
(3") The oxidation and reduction skeletal half-reactions are:

(4") Balance half-reactions with H+ and H2O:
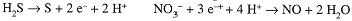
Multiply the coefficients of the first equation by 3 and the second by 2, and add, canceling the electrons:
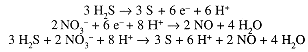
The H+ also cancel in part, leaving
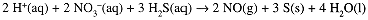
2 H+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 3 H2S(aq) → 2 NO(g) + 3 S(s) + 4 H2O(l)
(5) The two methods give the same result. Check that the atoms balance—2 N, 3 S, 6 O, and 8 H on each side—and that the charges balance—0 net charge on each side.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















