


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 27-8-2019
Date: 29-5-2017
Date: 28-7-2018
|
This is probably the single most important reaction of carboxylic acid derivatives. The overall transformation is defined by the following equation, and may be classified either as nucleophilic substitution at an acyl group or as acylation of a nucleophile. For certain nucleophilic reagents the reaction may assume other names as well. If Nuc-H is water the reaction is often called hydrolysis, if Nuc–H is an alcohol the reaction is called alcoholysis, and for ammonia and amines it is called aminolysis.
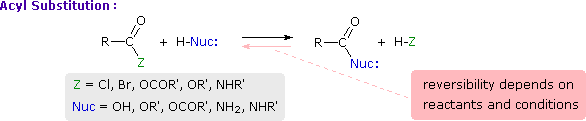
As illustrated in the following diagram, acylation reactions generally take place by an addition-elimination process in which a nucleophilic reactant bonds to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon atom to create a tetrahedral intermediate. This tetrahedral intermediate then undergoes an elimination to yield the products. In this two-stage mechanism bond formation occurs before bond cleavage, and the carbonyl carbon atom undergoes a hybridization change from sp2 to sp3 and back again. The facility with which nucleophilic reagents add to a carbonyl group was noted earlier for aldehydes and ketones.
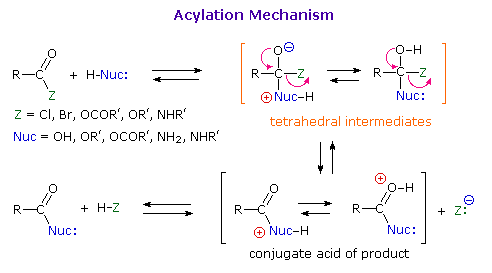



|
|
|
|
تحذير من "عادة" خلال تنظيف اللسان.. خطيرة على القلب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دراسة علمية تحذر من علاقات حب "اصطناعية" ؟!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تحذّر من خطورة الحرب الثقافية والأخلاقية التي تستهدف المجتمع الإسلاميّ
|
|
|