


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 16-6-2019
Date: 11-3-2017
Date: 21-7-2020
|
The original electronegativity scale, developed in the 1930s by Linus Pauling (1901– 1994) was based on measurements of the strengths of covalent bonds between different elements. Pauling arbitrarily set the electronegativity of fluorine at 4.0 (although today it has been refined to 3.98), thereby creating a scale in which all elements have values between 0 and 4.0.
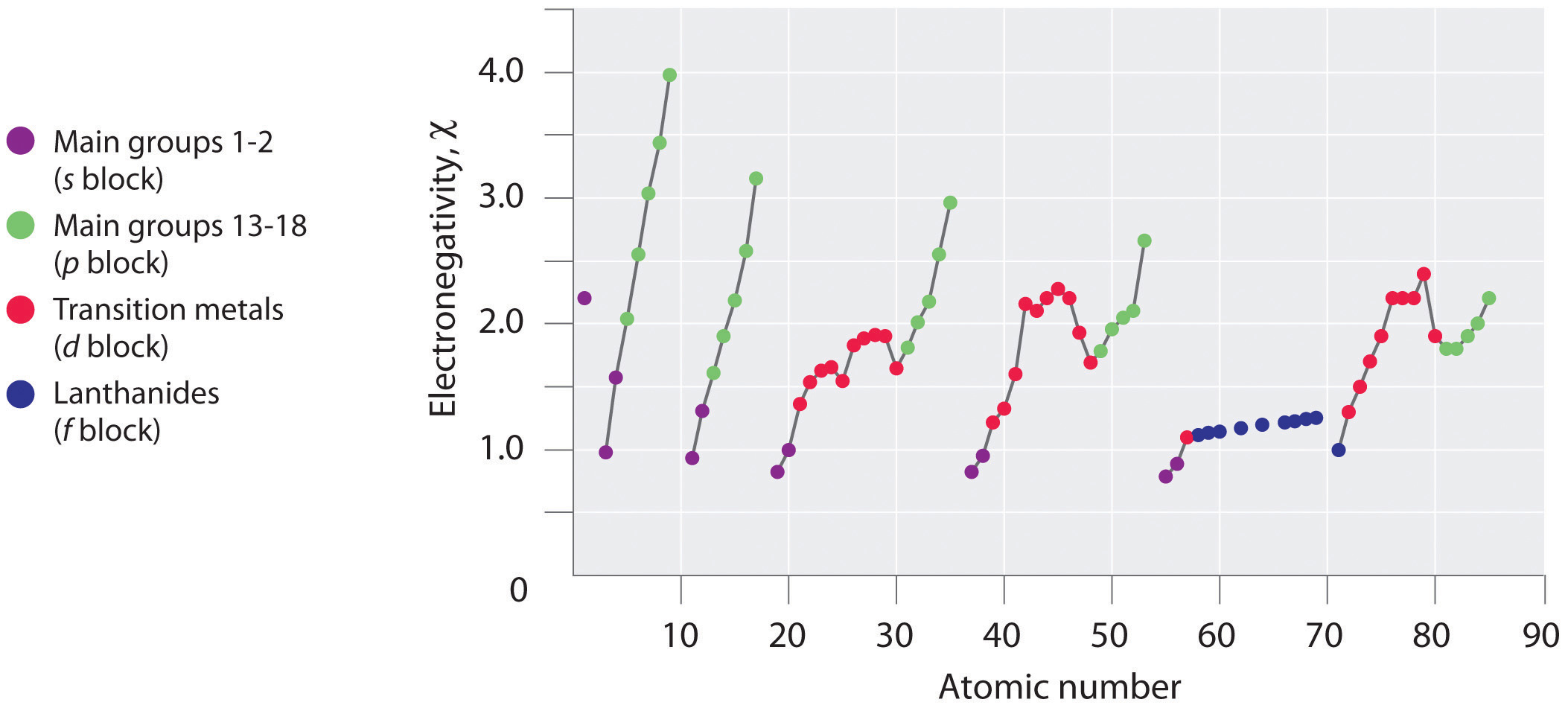
Figure 1 : A Plot of Periodic Variation of Electronegativity with Atomic Number for the First Six Rows of the Periodic Table
Periodic variations in Pauling’s electronegativity values are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2. If we ignore the inert gases and elements for which no stable isotopes are known, we see that fluorine (χ=3.98) is the most electronegative element and cesium is the least electronegative nonradioactive element (χ=0.79 ). Because electronegativities generally increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right of the periodic table, elements lying on diagonal lines running from upper left to lower right tend to have comparable values (e.g., O and Cl and N, S, and Br).
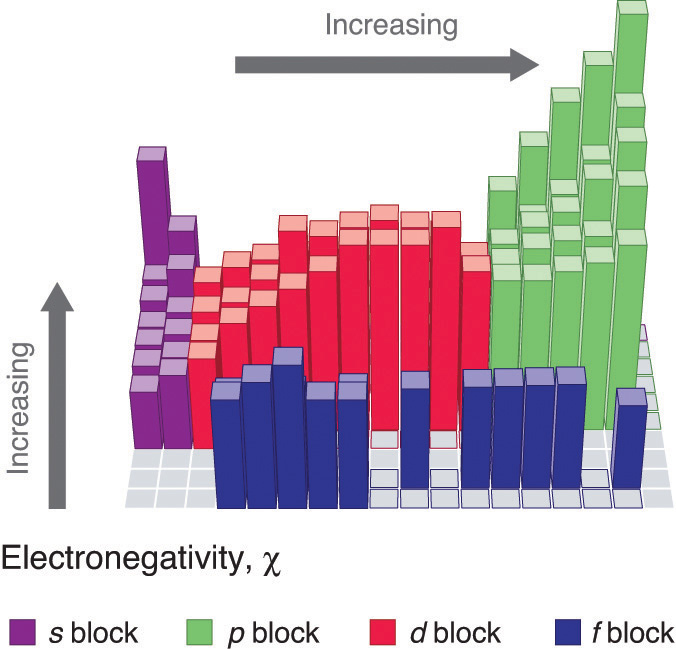
Figure 2 : Pauling Electronegativity Values of the s-, p-, d-, and f-Block Elements. Values for most of the actinides are approximate. Elements for which no data are available are shown in gray. Source: Data from L. Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd ed. (1960).
Linus Pauling (1901-1994)
When he was nine, Pauling’s father died, and his mother tried to convince him to quit school to support the family. He did not quit school, but was later denied a high school degree, and had to work several jobs to put himself through college. Pauling would go on to become one of the most influential chemists of the century if not all time. He won two Nobel Prizes, one for chemistry in 1954 and one for peace in 1962.
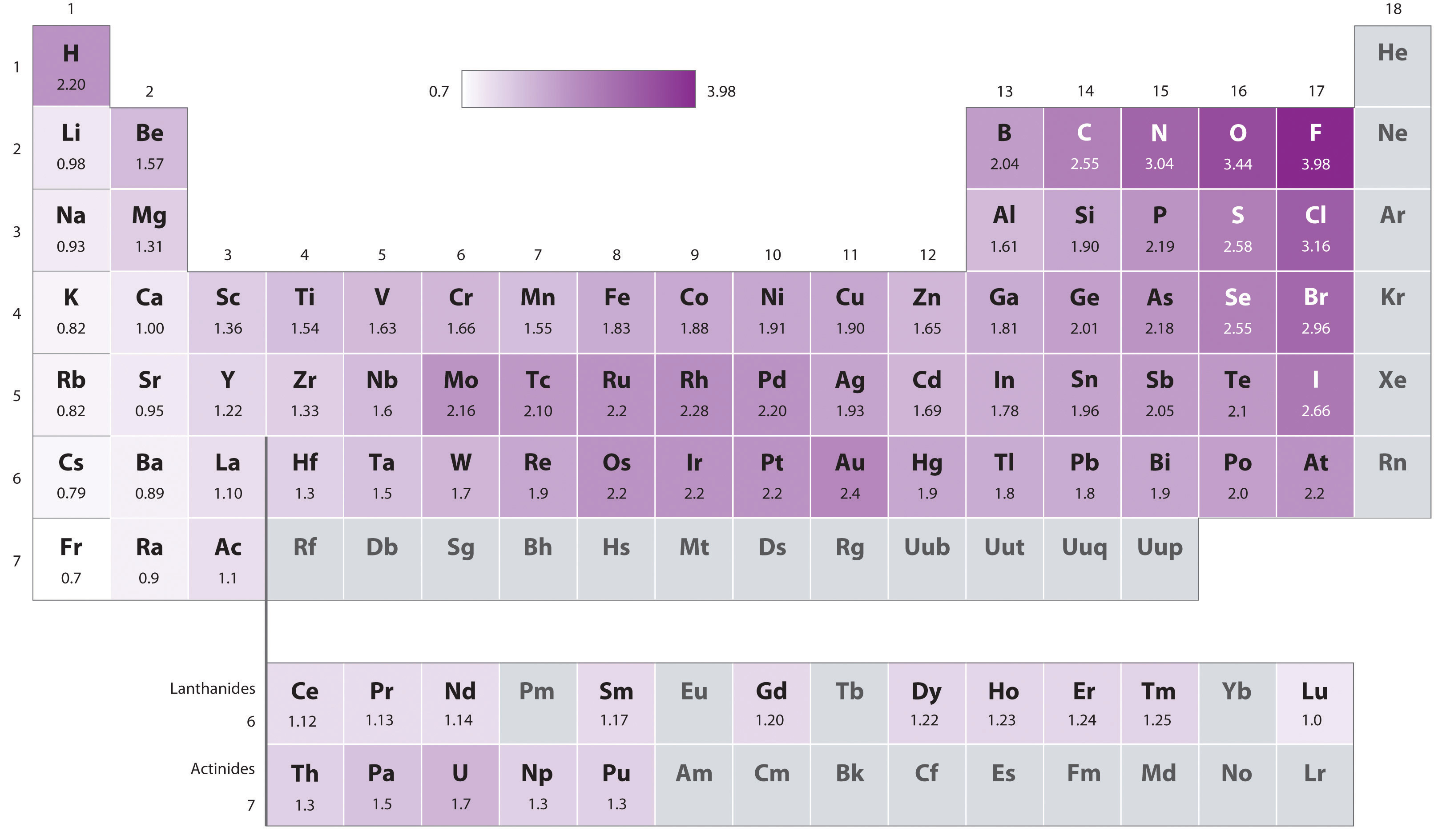
Pauling’s method is limited by the fact that many elements do not form stable covalent compounds with other elements; hence their electronegativities cannot be measured by his method. Other definitions have since been developed that address this problem, e.g., the Mulliken, Allred-Rochow, and Allen electronegativity scales. The Mulliken electronegativity of an element is the average of its first ionization energy and the absolute value of its electron affinity, showing the relationship between electronegativity and these other periodic properties.



|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل: شراكتنا مع المؤسّسات الرائدة تفتح آفاقًا جديدة للارتقاء بجودة التعليم الطبّي في العراق
|
|
|