
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
LASER HeNe STRUCTURE
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
الجزء والصفحة:
p239
22-3-2016
2122
LASER HeNe STRUCTURE
Figure 1.1 shows a typical HeNe tube and a diagram of its principal features. This tube, typical of any modern HeNe tube built by any major manufacturer, features integral cavity optics sealed right into the tube. Other than the initial alignment at the factory, no other adjustments are required for the life of the tube. The anode

(a)
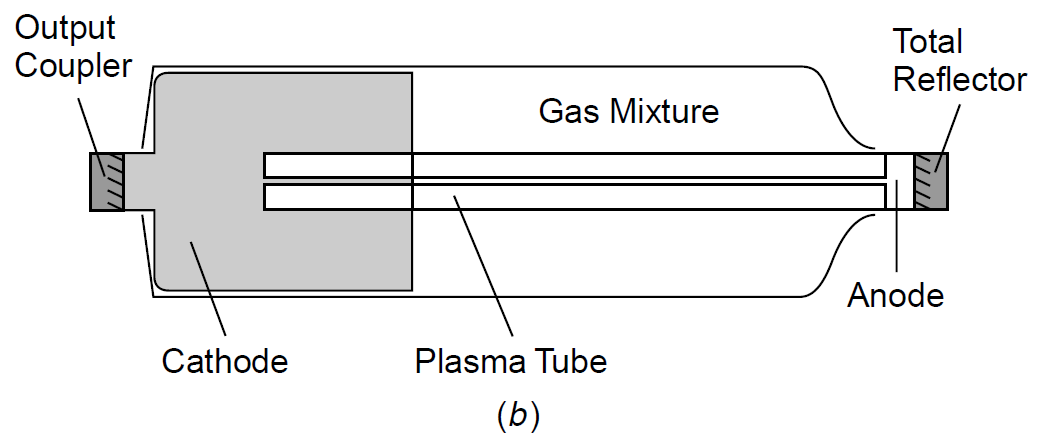
Figure 1.1. Typical HeNe tube and structures.
of the tube is small (in older HeNe tubes it was a metal pin), while the cathode is quite large and is contained inside a large gas ballast volume. As the tube operates, gas molecules are pumped toward the anode, increasing the pressure at the anode. Without the large ballast volume the gas pressure at the cathode becomes very low and the discharge becomes unstable. In some lasers, such as argons, a gas return path is provided to equalize gas pressures in the tube; however, HeNe tubes simply use a large ballast volume.
The cathode itself is usually made of high-purity aluminum, and in fact the necessity for purity in tube materials as well as gas mixture is quite extreme. Gas purity is crucial since even small amounts (< 1%) of impurities, such as water vapor or hydrogen, will drastically decrease power in the tube and cause lasing to cease entirely. Older HeNe tubes used mirrors that were epoxied to the glass tube. Such tubes, called soft-sealed tubes, typically had short lives, since helium diffuses through epoxy at a slow, albeit significant rate. Over the course of a few years the gas mix in the tube became short on helium and the lasers would cease to operate. This process could be exploited in reverse to resurrect outgassed tubes by placing the tube into a chamber of pure helium, which would eventually diffuse back into the tube. By the 1980s, tubes were manufactured with hard glass-to-metal seals, essentially eradicating the problem.1 Processing is still an example of where high purity is required, though. Extreme care must be taken to rid tubes of impurities (usually, through multiple bake-out cycles) before finally filling them with a high-purity gas mixture and sealing the tube.
HeNe tubes can vary in length from under 12 cm to over 1 m. The smallest tubes easily fit, along with a compact power supply, into handheld bar-code scanners and produce around 1 mW (although for this application semiconductor lasers are now often used). The largest units, like that pictured in Figure 1.2, sport tubes over 1 m long and are used for research and holography purposes, producing about 120 mW of red output. Long tubes such as these also have higher gains, allowing the use of wavelength selectors to lase one of several possible wavelengths (although the gain is still generally too low to allow multiline operation as is commonly done with argon lasers).
While most HeNe tubes have integral mirrors, a few (usually, research lasers like the one used in many experiments throughout this book) have external mirrors. In this case the ends of the plasma tube are either terminated with Brewster windows or with plane antireflection (AR)-coated windows. Such AR coatings are required since light passing through an uncoated plane window will incur a loss of about 4% per surface (or 8% in total). Most small HeNe tubes sport a gain of about 0.12 to 0.15 m-1, so a tube 30 cm in length has a gain of only about 4 to 5%. Losses of 16% (two windows) would be completely intolerable! External optics are mounted on a heavy frame or optical bench with optomechanical mounts allowing adjustment in either (horizontal or vertical) direction. Often, dust covers are

Figure 1.2. Large HeNe lab laser.
installed between windows and mirrors to keep the necessity for cleaning the laser optics to a minimum (in a low-gain laser, dust on a window may be enough to extinguish oscillation). If used on a tube with external optics, Brewster windows also serve to polarize the output beam. Some tubes feature internal Brewster windows placed within the tube (usually, within one of the metal stems protruding from the tube), solely for the purpose of polarization.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















