


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 2025-01-08
Date: 2025-01-08
Date: 2025-01-02
|
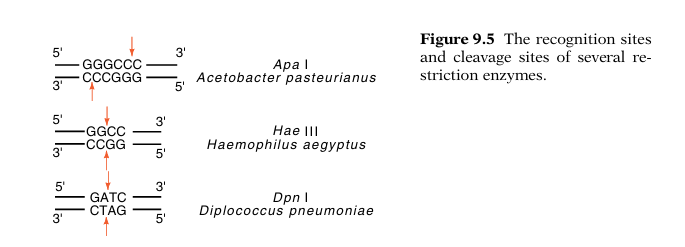
The restriction enzymes provide a necessary tool for cutting fragments of DNA out of larger molecules. Their exquisite specificity permits very great selectivity, and because more than one hundred different restriction enzymes are known, their wide variety permits much choice in the cleavage sites utilized. Often, fragments may be produced with end points located within 20 base pairs of any desired location. One of the more useful properties of restriction enzymes for genetic engineering is found in the restriction-modification system produced by the E.coli plasmid R. The corresponding restriction enzyme is called EcoRI.
Instead of cleaving at the center of its palindromic recognition sequence, this enzyme cleaves off-center and produces four base self complementary ends. These “sticky” ends are most useful in recombinant DNA work as they can be reannealed at low temperatures like the “sticky” ends of phage lambda. This permits efficient joining of DNA fragments during ligation steps. About half of the restriction enzymes now known generate overhanging or sticky ends. In some situations, a DNA fragment can even be arranged to have two different types of sticky ends so that its insertion into another DNA can be forced to proceed in one particular orientation.




|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|