

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Tin and lead halides
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
361
2025-09-06
105
Tin and lead halides
Key points: Tin forms dihalides and tetrahalides; for lead, only the dihalides are stable. Aqueous and nonaqueous solutions of tin (II) salts are useful mild reducing agents, but they must be stored under an inert atmosphere because air oxidation is spontaneous and rapid:
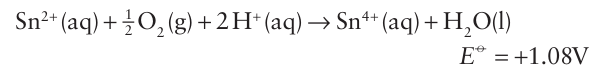
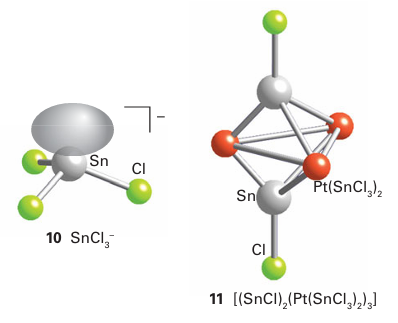
Tin dihalides and tetrahalides are both well known. The tetrachloride, tetrabromide, and tetraiodide are molecular com pounds, but the tetrafluoride is an ionic solid formed from close as an ionic solid but, as a manifestation of the inert-pair effect, PbCl4 is an unstable, covalent, yellow oil that decomposes into PbCl2 and Cl2 at room temperature. Lead tetrabromide and tetraiodide are unknown, so the dihalides dominate the halogen compounds of lead. The arrangement of halogen atoms around the central metal atom in the dihalides of tin and lead often deviates from simple tetrahedral or octahedral coordination and is attributed to the presence of a stereochemically active lone pair. The tendency to achieve the distorted structure is more pronounced with the smallion, and less distorted structures are observed with larger halides. Both Sn (IV) and Sn (II) form a variety of complexes. Thus, SnCl4 forms complex ions such as SnCl5 and SnCl6 -2 in acidic solution. In nonaqueous solution, a variety of donors interact with the moderately strong Lewis acid SnCl4 to form complexes such as cis-SnCl4 (OPMe3 )2. In aqueous and nonaqueous solutions Sn (II) forms trihalo complexes, such as SnCl3, where the pyramidal structure indicates the presence of a stereochemically active lone pair (10). The SnCl3 ion can act as a soft donor to d-metal ions. One unusual example of this ability is the red cluster compound Pt3 Sn8Cl20, which is trigonal bipyramidal (11).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















