

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Azides
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
382
2025-09-07
57
Azides
Key points: Azides are toxic and unstable; they are used as detonators in explosives. Azides, in which nitrogen is present as N3, may be synthesized by the oxidation of sodium amide with either NO3− ions or N2O at elevated temperatures:
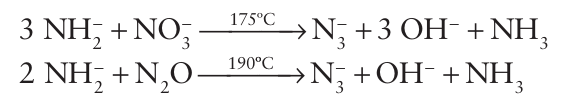
The average oxidation number of N in the azide ion is – . The ion is isoelectronic with both dinitrogen oxide, N2O, and CO2 and, like these two molecules, is linear. It is a reasonably strong Brønsted base, the pKa of its conjugate acid, hydrazoic acid, HN3, being 4.77. It is also a good ligand towards d-block ions. However, heavy-metal complexes or salts, such as Pb(N3)2 and Hg(N3)2, are shock-sensitive detonators and decompose to pro duce the metal and nitrogen:
. The ion is isoelectronic with both dinitrogen oxide, N2O, and CO2 and, like these two molecules, is linear. It is a reasonably strong Brønsted base, the pKa of its conjugate acid, hydrazoic acid, HN3, being 4.77. It is also a good ligand towards d-block ions. However, heavy-metal complexes or salts, such as Pb(N3)2 and Hg(N3)2, are shock-sensitive detonators and decompose to pro duce the metal and nitrogen:
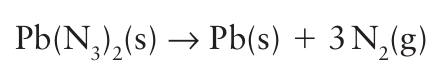
Ionic azides such as NaN3 are thermodynamically unstable but kinetically inert; they can be handled at room temperature. Sodium azide is toxic and is used as a chemical preservative and in pest control. When alkali metal azides are heated or detonated by impact they explode, liberating N2; this reaction is used in the inflation of air bags in cars, in which the heating of the azide is electrical. A brief illustration. A typical airbag contains approximately 50 g of NaN3. To estimate the volume of nitrogen produced when the azide is detonated at room temperature and pressure (20C and 1.0 atm) we need to consider the amount (in moles) of N2 molecules produced in the decomposition reaction 2NaN3(s) → 2Na(s)+3N2 (g). Because 50 g of NaN3 contains 0.77 mol NaN3, it liberates 1.2 mol N2. This amount occupies 26 dm3 at 20C and 1.0 atm. As the airbag is restricted in volume, the pressure of nitrogen in the airbag will be high, so providing protection to the driver.
Compounds containing the polynitrogen cation, N5+ (11), have been synthesized from species containing N3− and N2 F ions. For example, N5 AsF6 is prepared from N2FAsF6 and HN3 in anhydrous HF solvent:
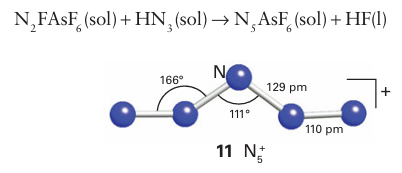
The compound is a white solid that decomposes explosively above 250ºC. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and ignites organic material even at low temperatures. Salts of dipositive anions can be prepared from metathesis with the salts of monopositive anions in anhydrous HF:
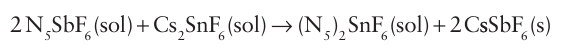
The product is a white solid that is friction-sensitive and decomposes to N5 SnF6 above 250ºC. This product, N5 SnF6, is stable up to 500ºC.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















