

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Compounds with nitrogen
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص365-366
2025-09-06
89
Compounds with nitrogen
Key points: The cyanideion, CN, forms complexes with many d-metal ions; its coordination to the active sites of enzymes such as cytochrome c oxidase accounts for its high toxicity. Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, is produced in large amounts by the high-temperature catalytic partial oxidation of methane and ammonia, and is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many common polymers, such as poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly(acrylonitrile). It is highly volatile (b.p. 26°C) and, like the CN ion, highly poisonous. In some respects the toxicity of the CN ion is similar to that of the isoelectronic CO molecule because both form complexes with iron porphyrin molecules. However, whereas CO attaches to the Fe in haemoglobin and causes oxygen starvation, CN targets the Fe in the active site of cytochrome c oxidase (the enzyme in mitochondria that reduces oxygen to water), which results in a rapid and catastrophic col lapse of energy production.
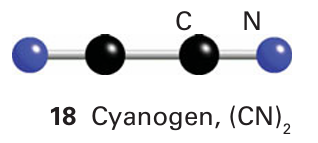
Unlike the neutral ligand CO, the negatively charged CN ion is a strong Brønsted base (pKa=9.4) and a much poorer Lewis acid π acceptor. The CO ligand can form complexes with met als in a zero-oxidation state as it can remove electron density through the π system. However, the coordination chemistry of CN is more often associated with metal ions in positive oxidation states, as with Fe2 in the hexacyanoferrate (II) complex, [Fe(CN)6]4- , as there will be less electron density on the metal ion. The toxic, flammable gas cyanogen, (CN)2 (18), is known as a pseudohalogen because of its similarity to a halogen. It dissociates to give .CN radicals and forms interpseudohalogen com pounds, such as FCN and ClCN. Similarly, CN is an example of a pseudohalide ion (Section 17.7).
The direct reaction of Si and N2 at high temperatures pro duces silicon nitride, Si3N4. This substance is very hard and in-ert, and is used in high-temperature ceramic materials. Current industrial research projects focus on the use of suitable organo silicon nitrogen compounds that might undergo pyrolysis to yield silicon nitride fibres and other shapes. When SiO2 is heated with carbon, CO is evolved and silicon carbide, SiC, forms. This very hard material is widely used as the abrasive carborundum.Trisilylamine, (H3Si)3 N, the silicon analogue of trimethylamine, has very low Lewis basicity. It has a planar structure, or is fluxional with a very low barrier to inversion. The low basicity and planar structure have traditionally been attributed to d-orbital participation in bonding, allowing sp2 hybridization around the N atom and delocalization of the lone pair through π bonding. However, quantum mechanical calculations indicate that whereas d orbit als play a role in delocalization, they are not responsible for the planar structure. Because the electronegativity of Si is lower than that of C, the Si-N bond is more polar than the C-N bond. This difference leads to long-range electrostatic repulsion between the silyl groups in trisilylamine and hence a planar structure.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















