

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Ammonia
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص383-384
2025-09-07
59
Ammonia
Key points: Ammonia is produced by the Haber process; it is used to manufacture fertilizers and many other useful nitrogen-containing chemicals. Ammonia is produced in huge quantities worldwide for use as a fertilizer and as a primary source of nitrogen in the production of many chemicals. As already mentioned, the Haber process is used for the entire global production. In this process, N2 and H2 combine directly at high temperature (450ºC) and pressure (100 atm) over a promoted Fe catalyst:
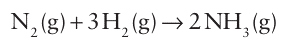
The promoters (compounds that enhance the catalyst’s activity) include SiO2, MgO, and other oxides (Section 26.12). The high temperature and catalyst are required to overcome the kinetic inertness of N2, and the high pressure is needed to overcome the thermodynamic effect of an unfavourable equilibrium constant at the operating temperature. So novel and great were the chemical and engineering problems arising from the then (early twentieth century) uncharted area of large-scale high-pressure technology, that two Nobel Prizes were awarded in connection with the process. One went to Fritz Haber (in 1918), who developed the chemical process. The other went to Carl Bosch (in 1931), the chemical engineer who designed the first plants to realize Haber’s process. The Haber Bosch process has had a major impact on civilization because ammonia is the primary source of most nitrogen-containing compounds, including fertilizers and most commercially important compounds of nitro gen. Before the development of the process the main sources of nitrogen for fertilizers were guano (bird droppings) and saltpetre, which had to be mined and transported from South America. In the early twentieth century there were predictions of widespread starvation across Europe, predictions that were never realized because of the widespread availability of nitrogen-based fertilizers. The boiling point of ammonia is 33ºC, which is higher than that of the hydrides of the other elements in the group and indicates the influence of extensive hydrogen bonding. Liquid ammonia is a useful nonaqueous solvent for solutes such as alcohols, amines, ammonium salts, amides, and cyanides. Reactions in liquid ammonia closely resemble those in aqueous solution, as indicated by the following autoprotolysis equilibria:
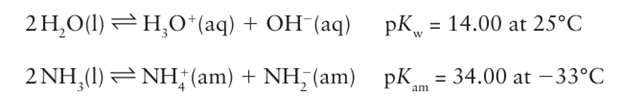
Many of the reactions are analogous to those carried out in water. For example, simple acid base neutralization reactions can be carried out:
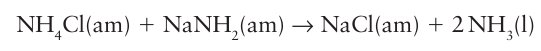
Ammonia is a water-soluble weak base:
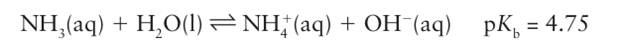
The chemical properties of ammonium salts are very similar to those of Group 1 salts, especially of K and Rb. They are soluble in water and solutions of the salts of strong acids, such as NH4 Cl, are acidic due to the equilibrium:
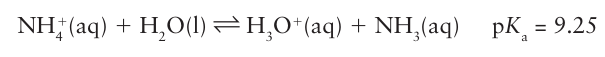
Ammonium salts decompose readily on heating and for many salts, such as the halides, carbonate, and sulfates, ammonia is evolved:
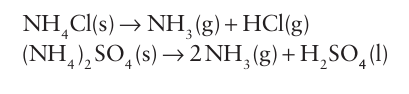
When the anion is oxidizing, as in the case of NO3−, ClO4−, and Cr2O72−, the NH4 is oxidized to N2 or N2O:
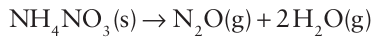
When ammonium nitrate is heated strongly or detonated, the decomposition of 2 mol NH4NO3 (s) in the reaction
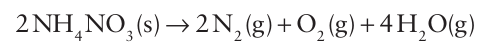
produces 7 mol of gaseous molecules, corresponding to an increase in volume from about approximately 200 cm3 to about 140 dm3, a factor of 700. This feature leads to the use of am monium nitrate as an explosive and nitrate fertilizers are often mixed with materials such as calcium carbonate or ammonium sulfate to make them more stable. Ammonium sulfate and the ammonium hydrogenphosphates, NH4H2 PO4 and (NH4)2HPO4, are also used as fertilizers because phosphate is a plant nutrient. Ammonium perchlorate is used as the oxidizing agent in solid fuel rocket propellants.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















