
Friction
 المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
 المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 80
الجزء والصفحة:
p 80
 15-12-2016
15-12-2016
 3008
3008
There are two types of friction static and kinetic. When two surfaces are in relative motion then the friction is kinetic, such as when you slam the brakes on in your car and the car skids along the road. Eventually, kinetic friction will cause the car to stop. If you put a coin on top of a book and tilt the book at a small angle, the coin will remain stationary. Static friction prevents the coin from sliding. Tilt the book a bit more and still the coin does not slide. The static friction has increased to keep the coin in place. Eventually however, static friction will be overcome and the coin will slide down the book (with kinetic friction operating). Notice that the maximum amount of static friction occurred just before the coin started to slide.
Properties of Friction
If you press down hard on the coin, then the friction force will increase. When you press down you are causing the normal force N to get bigger. Thus friction is proportional to N. The proportionality constant is called the coeffcient of friction μ. The kinetic friction force fk is given by
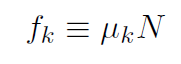
where μk is the coeffcient of kinetic friction. We saw that static friction varies. However the maximum value of the static friction force fs,max is

Both of these equations can be regarded as definitions for μk and μs.
Example The coeffcient of static friction is just the tangent of the angle where two objects start to slide relative to each other. Show that μs = tan µ.
Solution A force diagram is shown in Fig. 1.1.
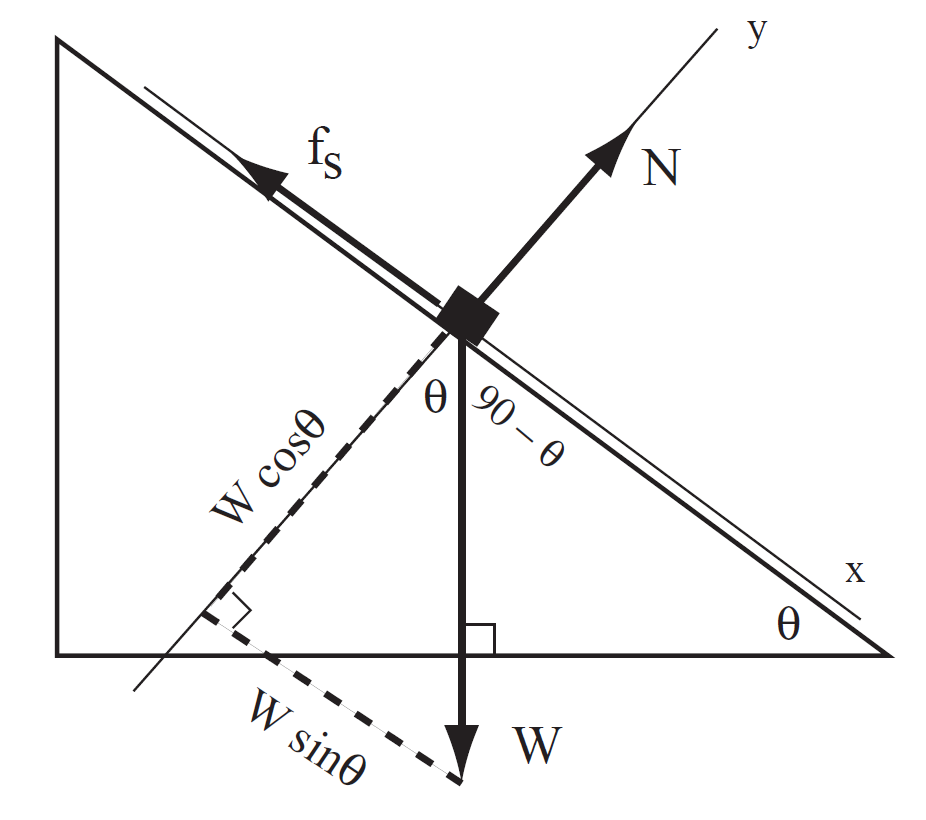
FIGURE 1.1 Block sliding down incline with friction.
Analyze forces in y direction

In x direction

where ax = 0 just before object starts to slide. Now we get N from y equation above (N = cos θ). Thus
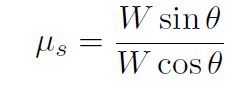
or
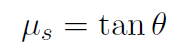
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


