
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Elastic Collisions in 1-dimension
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
p 120
28-12-2016
2937
Elastic Collisions in 1-dimension
Recall our work energy theorem for a single particle,
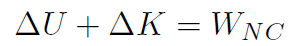
or
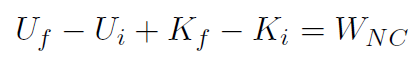
or
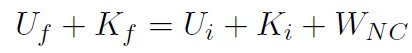
If WNC ≠ 0 then energy will not be conserved. For a two-body collision process, then an inelastic collision is one in which energy is not conserved (i.e. WNC ≠ 0), but an elastic collision is one in which energy is conserved (WNC = 0). Now if you think of a collision of two billiard balls on a horizontal pool table then Uf = mgyf and Ui = mgyi, but yf = yi and thus Uf = Ui or ΔU = 0. Thus the above work-energy theorem would be
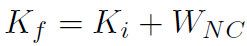
Thus for collisions where Ui = Uf , we often say more simply that an elastic collision is when the kinetic energy alone is conserved and an inelastic collision is when it is not conserved. In this section we first will deal only with elastic collisions in 1-dimension.
Example A billiard ball of mass m1 and initial speed v1i hits a stationary ball of mass m2. All the motion occurs in a straight line. Calculate the final speeds of both balls in terms of m1, m2, v1i, assuming the collison is elastic (Is this a good assumption?).
Solution All the motion is in 1-dimension and so conservation of momentum (with v2i = 0) is just
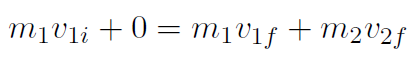
and conservation of kinetic energy is
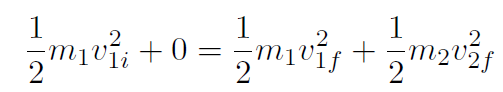
Here we have two equations with the two unknowns v1f and v2f . Thus the rest of the problem is simply doing some algebra. Let's solve for v1f in the first equation and then substitute into the second equation to get v2f. Thus
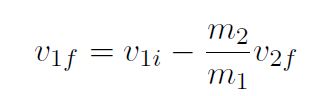
or

Substituting this into the conservation of kinetic energy equation gives
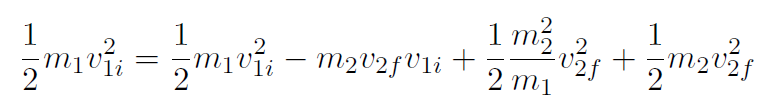
which simplifies to
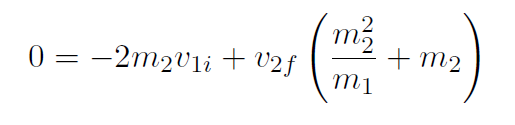
giving

which is finally
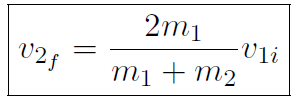
Substituting this back into the conservation of momentum equation gives
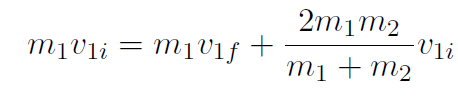
which gives
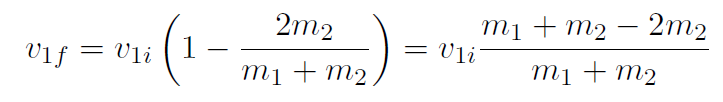
or
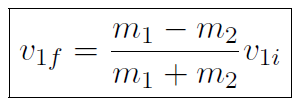
There are some interesting special situations to consider.
1) Equal masses (m1 = m2). This implies that v1f = 0 and v2f = v1i. That is the projectile billiard ball stops and transfers all of its speed to the target ball. (This is also true if the target is moving.)
2) Massive target (m2 >> m1). In this case we get v1f 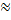 -v1i and
-v1i and 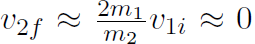 which means the projectile bounces off at the same speed and the target remains stationary.
which means the projectile bounces off at the same speed and the target remains stationary.
3) Massive projectile (m1 >> m2). Now we get v2f 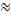 -v2i and v1f
-v2i and v1f 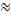 -v1i meaning that the projectile keeps charging ahead at about the same speed and the target moves off at double the speed of the projectile.
-v1i meaning that the projectile keeps charging ahead at about the same speed and the target moves off at double the speed of the projectile.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















