
The Rotational Variables
 المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
 المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 132
الجزء والصفحة:
p 132
 28-12-2016
28-12-2016
 2633
2633
The Rotational Variables
Previously we denoted translational position in 1-dimension with the symbol x. If a particle is located on the rim of a circle we often use s instead of x to locate its position around the circumference of the circle. Thus s and x are equivalent translational variables
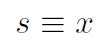
Now the angular position is described by angle which is defined as
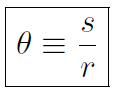
where s (or x) is the translation position and r is the radius of the circle. Notice that angle has no units because s and r both have units of m. The angle defined above is measured in radian, but of course this is not a unit. One complete revolution is 2π radian often also called 360o. (All students should carefully read Pg. 240 of Halliday for a clear distinction between radian and degrees.) Translational position is given by x (or s) and translation displacement was Δx ≡ x2 - x1 (or Δs ≡s2 - s1). Similarly angular displacement is
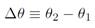
and because 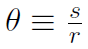 then it is related to translation displacement by
then it is related to translation displacement by

This is the first entry in the Master Table. Secondly we defined translational average velocity as 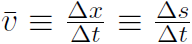 and instantaneous velocity as
and instantaneous velocity as 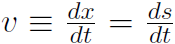 . Similarly we define average angular velocity as
. Similarly we define average angular velocity as

and instantaneous velocity as
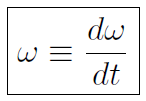
Now because we have 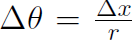 we must also have
we must also have 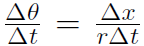 or
or 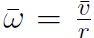 as relating average velocity and average angular velocity. Similarly
as relating average velocity and average angular velocity. Similarly
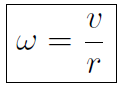
This is the second entry in the Master Table. Finally the angular acceleration α is defined as
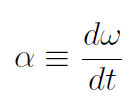
and

relating angular acceleration α to translational acceleration at. (Notice that a is not the centripetal acceleration. For uniform circular motion α = 0 and at = 0 because the particle moves in a circle at constant speed v and the centripetal acceleration is 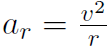 . For non-uniform circular motion, where the speed keeps increasing (or decreasing) then α ≠ 0 and a ≠ 0).
. For non-uniform circular motion, where the speed keeps increasing (or decreasing) then α ≠ 0 and a ≠ 0).
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


