
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Repeated Wave Forms
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المصدر:
Physics 2000
الجزء والصفحة:
439
4-12-2020
2441
Repeated Wave Forms
Before we apply the Fourier transform capability of MacScope to the analysis of experimental data, there is one more feature of the analysis we need to discuss. What we are doing with the program is reconstructing a selected section of a waveform from harmonic sine waves. Anything we build from harmonic sine waves exactly repeats at the period of the first harmonic. Thus our reconstructed wave will always be a repeating wave, beginning again at the same height as the beginning of the previous cycle.
You can most easily see what we mean if you select a non repeating section of a wave. In Figure (1) we have gone back to a sine wave, but selected one and a half cycles. In the FFT window you see a slew of harmonics. To see why these extra harmonics are present, we have in Figure (2) selected the first 9 of them and in the upper window see what they add up to. It is immediately clear what has gone wrong. The selected harmonics are trying to reconstruct a repeating version of our 1.5 cycle of the sine wave. The extra spurious harmonics are there to force the reconstructed wave to start and stop at the same height as required by a repeating wave. If you are analyzing a repeating wave form and select a section that repeats, then your harmonic reconstruction will be accurate, with no spurious harmonics. If
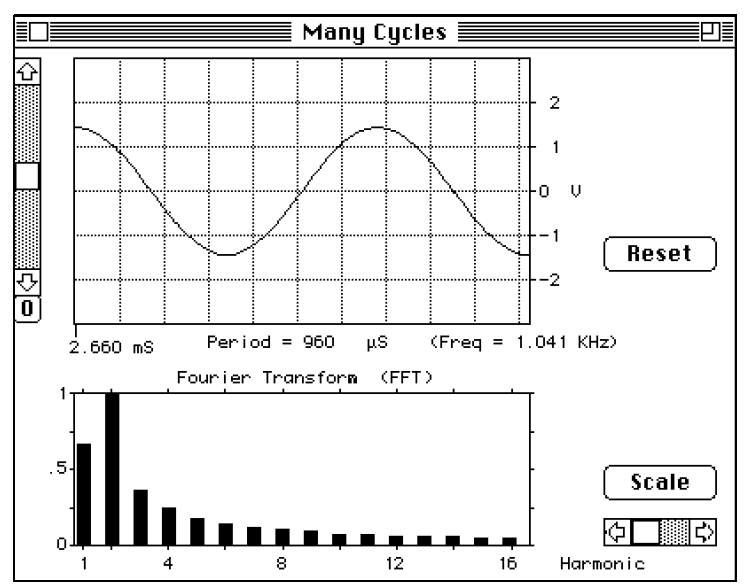
Figure 1: When we select one and a half cycles of a sine wave, we get a whole bunch of spurious harmonics.
your data is not repeating then you have to deal one way or another with this problem. One technique often used by engineers is to select a long section of data and smoothly force the ends of the data to zero so that the selected data can be treated as repeating data. Hopefully, forcing the ends of the data to zero does not destroy the information you are interested in. You can often accomplish the same thing by throwing away higher harmonics, assuming that the lower harmonics contain the interesting features of the data. You can see that neither of these techniques would work well for our one and a half cycles of a sine wave selected in Figure (2). In this text, our use of Fourier analysis will essentially be limited to the analysis of repeating waveforms. As long as we select a section that repeats, we do not have to worry about the spurious harmonics.
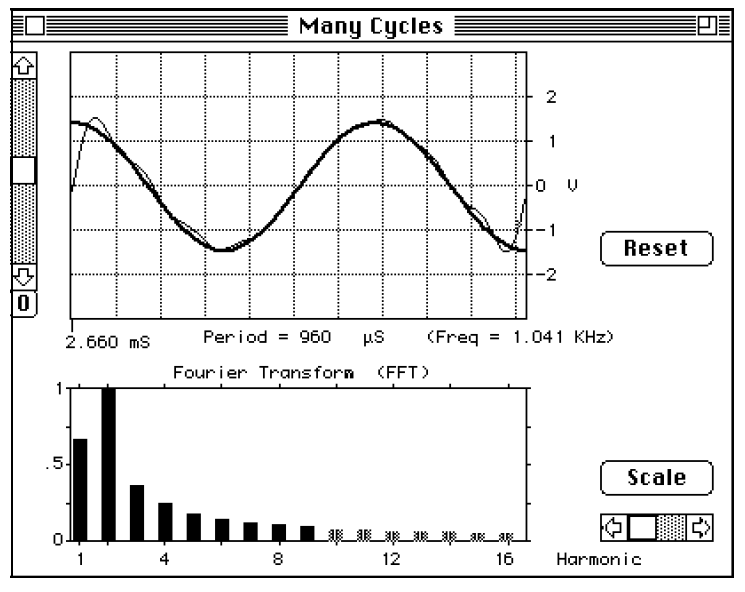
Figure 2: The spurious harmonics result from the fact that the reconstructed wave must be repeating—must start and stop at the same height.
 الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















